AI Agents are intelligent computer systems that monitor their environment, process information, make decisions, and take action to achieve specific goals in finance. Unlike regular programs, they can learn and direct themselves toward objectives. In finance, they operate in a complex world of market data, regulations, transactions, and customer interactions.
These agents work independently without constant human supervision. They adapt quickly to changes in the global market, maintain an internal state, understand their environment, and act purposefully to maximize goals like profit or minimize risk.
Key Takeaways:
- AI Agents enable real-time autonomous action through the Sense-Reason-Act loop
- Adoption is driven by massive data volumes and demand for personalized services
- Core benefits include operational efficiency, accuracy, and risk management
- Successful implementation requires data quality and clear governance
- Human oversight is essential for critical financial decisions
- The future involves collaborative Multi-Agent Systems and user-controlled agents
How Do AI Agents Improve Financial Services?
AI agents are transforming financial services in three fundamental ways: Automation, Optimization, and Personalization.
Automation frees human employees from repetitive tasks like data reconciliation, back-office processing, and regulatory reporting. This leads to faster turnaround times and lower operational costs.
Optimization improves the quality of complex financial decisions. This includes optimizing trading strategies, maximizing portfolio returns, or reallocating resources in response to market shifts.
Personalization transforms the customer experience. AI agents analyze customer data to offer tailored services like personalized budgeting advice, customized loan recommendations, or virtual financial coaching.
Why Are AI Agents Important in Modern Finance?
AI agents are transforming finance through their ability to process massive amounts of data and make decisions in real time. They respond to major shifts in how financial institutions operate and serve customers.
Key Drivers for Adoption
The rapid adoption of AI agents responds to profound shifts in the financial sector. The primary driver is the sheer volume and velocity of financial data. Traditional human analysis cannot keep pace with millions of transactions, market signals, and regulatory updates occurring every second.
A second crucial driver is the demand for personalized services from modern consumers. Customers expect financial institutions to understand their unique needs and offer tailored solutions. Only autonomous agents can perform this task effectively and at scale.
Global economic changes and evolving financial threats require adaptive and immediate responses. The pressure for cost reduction and increased efficiency compels institutions to move toward intelligent automation.
What Benefits Do AI Agents Provide in Financial Institutions?
The benefits of deploying AI agents are comprehensive. They impact everything from back-office operations to customer interactions.
Increased Operational Efficiency
AI agents automate high-volume, repetitive tasks that consume significant human labor and time. This includes automated data extraction, real-time reconciliation, and seamless handoffs between internal systems.
Agents execute these tasks with superior consistency and speed. They reduce workflow bottlenecks and lower the time required for processes like account opening from days to minutes.
Smarter, Data-Driven Decision-Making
AI agents leverage analytics against massive, diverse datasets. They identify connections that are hard to see, detect subtle market shifts, and analyze causal relationships invisible to human analysts.
In investment management, an agent incorporates real-time news sentiment and micro-transaction patterns to decide the optimal execution time for a trade.
Personalized Customer Experiences
AI agents enable true personalization at scale. They continuously analyze a customer’s entire financial footprint, including spending habits, savings goals, and risk tolerance.
They can proactively suggest a refinance opportunity, recommend an ideal investment mix, or offer personalized budgeting guidance. They often anticipate customer needs before customers express them.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Human error is inevitable in complex financial operations. AI agents operate based on code and mathematically validated models, ensuring superior accuracy.
When processing loan applications or monitoring Anti-Money Laundering transaction flows, agents apply rules consistently across millions of data points. This minimizes false positives in fraud detection and prevents reconciliation discrepancies.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
AI agents are essential tools for managing complex compliance burdens. Agents automatically monitor and interpret evolving regulatory texts like Know Your Customer and consumer protection laws.
They embed these rules directly into operational workflows. This ensures real-time adherence to global and regional mandates.
Cost Optimization and Revenue Growth
By handling tasks previously requiring large teams, AI agents reduce operational overhead and staffing costs. At the same time, agents drive revenue growth.
They identify cross-selling and up-selling opportunities through predictive analytics. This dual effect of lowering costs while increasing value per customer creates a powerful financial argument for agent adoption.
Scalability and Continuous Availability
AI agents operate around the clock. This ensures that services like fraud monitoring, customer support, and algorithmic trading remain active regardless of time or location.
During peak demand, institutions can instantly scale up the number of active agents without the delay or cost of hiring additional employees.
Where Are AI Agents Used in Finance?
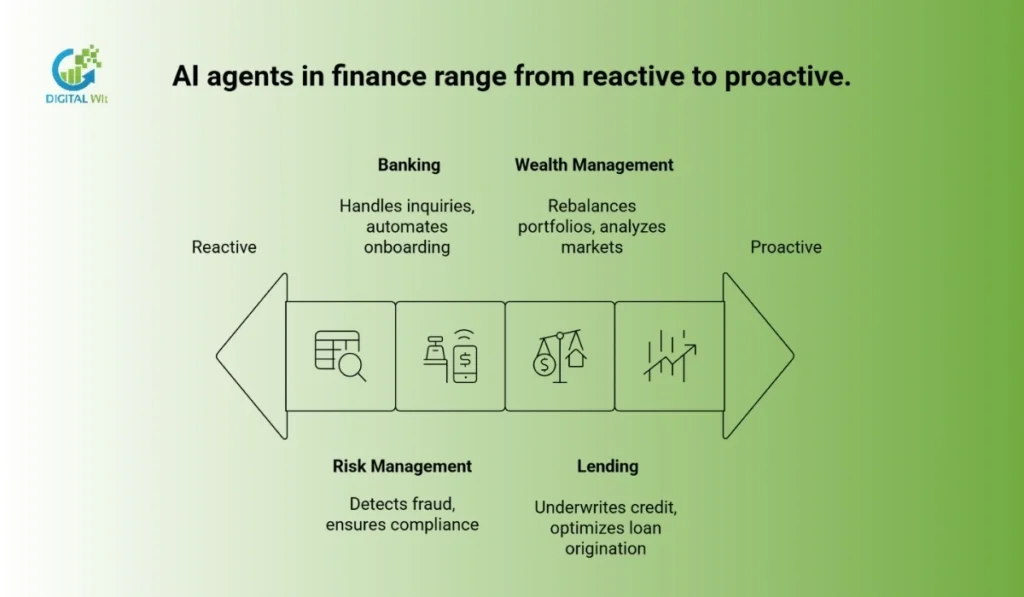
AI agents are deployed across every major area of the financial industry. They transform traditional processes into smart, autonomous workflows.
Risk Management and Compliance
Real-Time Fraud Detection
Agents continuously monitor millions of transactions in milliseconds. They analyze metadata like location, device, and transaction size, along with behavioral patterns to flag anomalies.
AI agents employ adaptive learning to detect novel fraud schemes like synthetic identity fraud or complex multi-channel attacks. Agents can automatically freeze a suspicious account or trigger a multi-factor authentication prompt.
Anti-Money Laundering and KYC
The Know-Your-Customer process is automated end-to-end. Agents gather and verify client documents, cross-check identities against global watchlists, and continuously monitor client behavior for suspicious money laundering patterns.
This automation can reduce customer onboarding time from days to minutes.
Regulatory Monitoring and Reporting
AI agents ingest and interpret complex, evolving regulatory texts like GDPR or MiFID II. They embed these rules directly into operational systems, ensuring real-time compliance.
They also automate the generation of audit-ready compliance reports.
Banking and Customer Service
AI agents are transforming how banks interact with customers. They provide instant, personalized service that works around the clock.
Intelligent Virtual Assistants
Agents handle routine banking inquiries instantly. This includes checking account balances, recent transactions, or fee structures.
Advanced conversational agents can offer personalized advice. They analyze a client’s spending patterns and recommend budget adjustments or savings strategies proactively.
Automated Customer Onboarding
Agents orchestrate the entire account opening process. They verify identity, cross-reference credit data, and ensure all required forms are complete.
This drastically improves the speed of the first customer interaction.
Collections Management
Agents manage overdue invoices and payments by automating communication via email or SMS. They track payment commitments and intelligently escalate accounts only when necessary.
Lending and Credit Underwriting
Agents speed up the traditionally slow process of assessing creditworthiness and loan approval. They handle complex data analysis in minutes instead of days.
Intelligent Credit Underwriting
For mortgages, auto loans, and small business loans, AI agents automatically gather and normalize vast amounts of applicant data. This includes credit reports, income verification, and alternative payment histories.
They apply dynamic credit risk models to calculate a risk score. They automatically approve eligible applications and provide detailed summaries for high-risk cases requiring human review.
Loan Origination Optimization
Agents streamline the entire loan lifecycle. They gather missing information, generate necessary forms, and manage communications across channels.
This ensures a fast and error-free process from application to disbursement.
Wealth Management and Investment
In investment, agents move beyond simple advice to full-scale portfolio management. They provide proactive, personalized strategies for every client.
Automated Portfolio Rebalancing
AI agents continuously monitor a client’s portfolio against their strategic targets, risk tolerance, and goals. When market movements cause the portfolio to drift beyond pre-set thresholds, the agent automatically generates and executes the necessary trades to rebalance the assets.
This ensures alignment without requiring constant human intervention.
Real-Time Market Analysis
Agents analyze high-velocity data streams including stock quotes, news sentiment, and macroeconomic indicators. They synthesize these factors to generate proactive investment recommendations or reassess asset valuations in real-time.
Personalized Investment Strategies
Agents leverage deep client profiling including tax status, ESG mandates, and income trends to tailor complex investment strategies. They also automate labor-intensive tasks like tax-loss harvesting and personalized performance reporting.
What Challenges Come With AI Agent Adoption?
While AI agents offer powerful capabilities, their deployment requires careful management. Institutions face technical, ethical, and regulatory hurdles that must be addressed.
Technical and Data Challenges
Data Quality and Integrity
AI agents are only as good as the data they consume. Poor quality data, inconsistencies, or gaps can lead to faulty reasoning and incorrect decisions.
Financial institutions must invest heavily in data governance and real-time data validation pipelines.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many banks rely on decades-old core banking systems that are difficult to connect with modern AI platforms. Agents require high-speed, reliable APIs to sense the environment and execute actions.
This makes system modernization a prerequisite.
Computational Scalability
Running multiple autonomous agents requires enormous computational resources. This is particularly true for large-scale operations like algorithmic trading or system-wide fraud detection.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The autonomous nature of AI agents creates new compliance and accountability concerns. These require careful governance and oversight.
Model Explainability
Financial regulators increasingly demand transparency, especially for high-impact decisions like loan approvals or fraud flags. If an AI agent automatically denies a loan, the institution must be able to explain the reasoning in clear terms.
Complex deep learning models often operate as “black boxes,” making explainability techniques essential for compliance.
Bias and Fairness
If training data reflects historical biases, the AI agent will perpetuate and scale that bias autonomously. Implementing agents requires continuous auditing for algorithmic fairness.
Institutions must use techniques to mitigate bias to ensure compliance with fair lending and equal opportunity regulations.
Accountability and Governance
When an autonomous agent makes a mistake that results in a significant financial loss or regulatory fine, determining accountability is difficult. Institutions must establish clear governance frameworks.
These define the scope of agent autonomy, human-in-the-loop oversight, and clear failover protocols.
Data Privacy and Security
AI agents handle massive volumes of sensitive personal information and transaction data. Compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA is paramount.
This requires secure data processing, anonymization, and robust security protocols to protect against breaches.
Strategic Implementation Steps
A successful transition to an agent-driven environment requires a phased approach. Institutions should focus on business outcomes and start small.
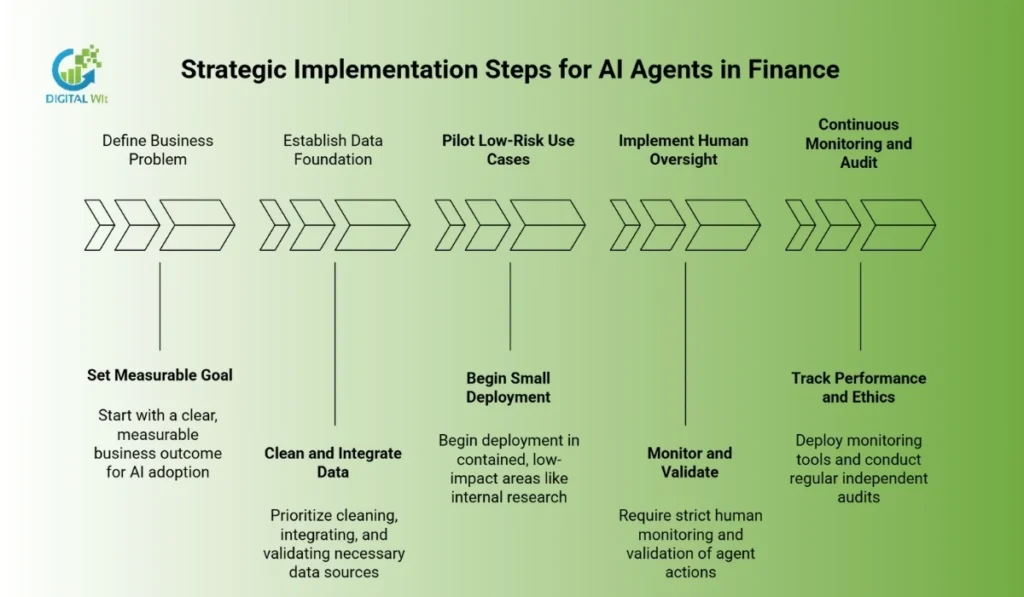
Define the Business Problem
Start with a clear, measurable goal. Instead of “implement AI,” target a specific outcome like “reduce credit card false positives” or “accelerate KYC from three days to 30 minutes.”
Establish Data Foundation
Prioritize cleaning, integrating, and validating the necessary data sources. Without high-quality data and robust APIs connecting to operational systems, agents cannot function.
Pilot with Low-Risk Use Cases
Begin deployment in contained, low-impact areas like internal research, document classification, or virtual Q&A. In these areas, an agent’s failure has minimal financial or regulatory risk.
Implement Human Oversight
Even for autonomous tasks, initial deployments require strict human monitoring. Establish clear thresholds for agent actions and use human analysts for final review and validation of high-impact decisions.
Continuous Monitoring and Audit
Deploy comprehensive monitoring tools to track the agent’s performance, resource consumption, and adherence to ethical standards. Regular, independent audits are essential.
How Will Financial AI Agents Evolve?
The evolution of AI agents is accelerating. The financial sector is moving from single, specialized agents to collaborative, intelligent ecosystems.
Multi-Agent Systems
Currently, most deployments involve a single agent performing a defined task. The future lies in Multi-Agent Systems, where different specialized agents coordinate to solve complex problems.
For example, a Customer Onboarding Agent could coordinate with a Compliance Agent to verify KYC, a Credit Agent to run underwriting models, and a Documentation Agent to generate final contracts.
Sovereign and Personalized Agents
As AI tools become more powerful, individuals will deploy their own personal agents. These assistants will act exclusively on the user’s behalf.
Imagine an agent that autonomously monitors all your investment, tax, and lending opportunities across different banks. It negotiates better interest rates, automatically optimizes your tax liabilities, and manages your budget across multiple digital wallets.
Advanced Tool and API Use
The capability of agents to reason and act will grow through access to complex tools. They will become versatile financial orchestrators.
Future agents will execute complex, multi-step financial maneuvers by accessing dozens of APIs. This includes market data providers, blockchain ledgers, and secure payment networks.
Generative Agents for Novel Products
Generative AI will transition from simply generating text to becoming the core reasoning engine for new products. This represents a fundamental shift in how financial innovation happens.
Generative Agents will be used to simulate future market conditions, design novel financial instruments like custom derivatives or insurance policies, and conduct testing on existing systems to find vulnerabilities.
Final Thoughts
AI agents are transforming finance by automating complex tasks, improving decision-making, and delivering real-time personalization. As institutions move toward intelligent, autonomous systems, adopting this technology becomes essential for staying competitive.
For businesses in Bangladesh seeking to integrate AI solutions, Digital Wit stands out as the best digital marketing agency in BD. Their expertise in AI implementation and digital transformation helps companies adopt intelligent automation safely and effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the main difference between an AI Agent and a standard Machine Learning model?
An ML model only predicts. An AI Agent predicts, reasons, and then takes action, completing the full Sense to Reason to Act cycle.
Q: How do institutions ensure fairness and reduce bias in AI Agents?
They use independent fairness audits, clean biased training data, and apply bias-mitigation techniques to prevent unfair outcomes in areas like lending or fraud checks.
Q: What is a Multi-Agent System (MAS), and why does it matter in finance?
MAS is a network of specialized agents working together (e.g., KYC Agent + Credit Agent). It speeds up complex workflows and removes operational silos.
Q: Can AI agents work with existing banking systems?
Yes, but integration requires proper APIs and system modernization. Many banks update their legacy systems to enable smooth AI agent deployment.
Q: How long does it take to implement AI agents in a financial institution?
Implementation time varies by use case. Simple pilots can start in weeks, while enterprise-wide deployment may take several months to a year.
Q: Do AI agents replace human employees?
AI agents handle repetitive tasks, allowing human employees to focus on complex decision-making, relationship building, and strategic work.
Q: What industries beyond finance can use AI agents?
AI agents are expanding to healthcare, retail, manufacturing, logistics, and customer service across multiple sectors.