Healthcare today struggles with serious challenges. Staff burnout, slow diagnoses, mountains of paperwork, and rising costs hurt hospitals and clinics everywhere. These problems hit especially hard in Bangladesh, where the gap between city and village healthcare makes everything worse.
Artificial Intelligence has evolved beyond simple data analysis. Today’s AI agents are smart, independent systems that can think and act on their own. They’re changing how we diagnose diseases, treat patients, and run medical facilities.
Key Takeaways
- AI agents are autonomous software systems that can reason, learn, and act independently to solve healthcare problems
- They improve diagnostic accuracy by analyzing medical images and patient data faster than traditional methods
- Virtual nurse agents and automated systems reduce administrative burden, freeing medical staff for direct patient care
- Personalized treatment plans use patient data from multiple sources to create tailored care strategies
- Workflow automation cuts costs and reduces clinician burnout by handling repetitive tasks
- Challenges include data privacy, algorithmic bias, regulatory compliance, and ensuring fair access across urban and rural areas
What Are AI Agents in Healthcare?
Medical AI agents are more than basic computer programs or chatbots. They are intelligent software systems designed to observe data, create plans, complete multiple task steps, and adjust their actions to reach specific healthcare goals.
Unlike older AI that follows fixed rules, intelligent agents can make decisions independently and use logic to solve complex problems. They don’t need constant human supervision.
Their core abilities include processing real-time medical data like images, lab results, and clinical notes. They connect symptoms to possible diagnoses through advanced reasoning. They suggest specific treatment paths and continuously learn from new results and feedback to improve accuracy.
Core Components of AI Agents in Healthcare
AI agents get their power from a well-designed structure that handles complicated tasks and remembers context across many interactions.
Reasoning Models serve as decision-making engines, often powered by advanced Large Language Models or deep learning systems. They link different information pieces, such as a patient’s genetic details and allergy history, to form clear diagnostic plans.
Memory and State Management allows agents to remember previous interactions and test results. A virtual nurse agent, for example, tracks past conversations and ensures care continues smoothly without repeated data entry.
Integration APIs connect agents with existing healthcare technology, including digital patient records, lab systems, and medical imaging databases. Strong APIs guarantee smooth, real-time data sharing.
Monitoring Interfaces give doctors and administrators clear views into agent actions and performance. They track success rates, time saved, and compliance with clinical rules to ensure safety and accountability.
Types of AI Agents Used in Healthcare
AI agents work across many different parts of the health system.
Diagnostic Scribe Agents listen to patient-doctor conversations and automatically create medical documents like discharge summaries or clinical notes. They pull relevant information from digital patient records instantly.
Predictive Analytics Agents constantly monitor hospital data to predict resource needs, such as bed allocation during a dengue outbreak. They identify patients at high risk of readmission and detect equipment that might fail soon.
Virtual Nurse Agents connect with patients to manage follow-up care, send automatic medication reminders, and answer common questions. This frees clinical staff from routine communication tasks.
Voice Agents handle administrative work like automatic appointment scheduling and patient intake using natural spoken language.
AI Agents in Diagnosis and Risk Prediction
AI agents are changing clinical practice by acting as powerful, objective assistants to doctors. Their main strength is faster and more precise analysis of complex patient data, especially in areas like medical imaging.
Current applications are widespread. Agents excel in radiology by quickly highlighting potential problems in X-rays or CT scans for doctor review. In pathology, they examine digital tissue slides to spot tiny cell patterns that suggest disease. In symptom triage, they process patient input and medical history to decide which urgent cases need immediate attention.
By performing real-time analysis and flagging serious issues, these agents boost diagnostic accuracy and greatly reduce human error. They support early discovery of chronic diseases.
A key ability of intelligent agents is Predictive Analytics and Risk Stratification. These autonomous agents constantly monitor and combine data points from lab results, vital signs, and background details to find subtle patterns that suggest future problems.
For example, an agent can calculate a patient’s personal risk of developing an infection, having post-surgery complications, or needing readmission. It sends quick alerts to the care team before a crisis happens. This shifts healthcare from reactive problem-solving to proactive prevention.
AI Agents in Treatment and Personalized Patient Care
AI agents provide dynamic support throughout the entire treatment process by making care truly personal and scalable.
Personalized Treatment Plans
AI agents sort through huge amounts of diverse data, including digital patient records, genomics, and lifestyle factors from smart devices. They create specific, individualized treatment plans by analyzing how well treatments worked for similar patient groups.
Crucially, they make adaptive treatment adjustments in real time. An agent monitoring a diabetic patient’s continuous glucose monitor and activity data can immediately suggest an insulin change or diet adjustment. This ensures care plans always respond quickly to current health status.
Behavioral and Chronic Health Support
A major impact area is autonomous support for managing long-term health. AI agents act as continuous virtual helpers, giving specialized support for mental health and chronic disease management.
For patients with conditions like high blood pressure or COPD, agents deliver automated reminders, offer encouraging advice, and check in regularly. They act as an extension of the clinical team. This continuous, low-cost monitoring greatly helps patients stick to their care plans and improves health outcomes.
Precision Medicine and Drug Discovery
AI agents are vital to the future of Precision Medicine. By processing detailed genetic data, agents figure out hyper-personalized drug dosing and fine-tune treatment rules for each patient. This dramatically reduces side effects and boosts effectiveness.
In the pharmaceutical industry, these agents accelerate drug development by simulating how molecules interact, predicting if a compound will work and if it’s safe, and finding the best candidates for clinical trials. This significantly reduces the time and cost of bringing new medicines to market.
AI Agents for Workflow Automation
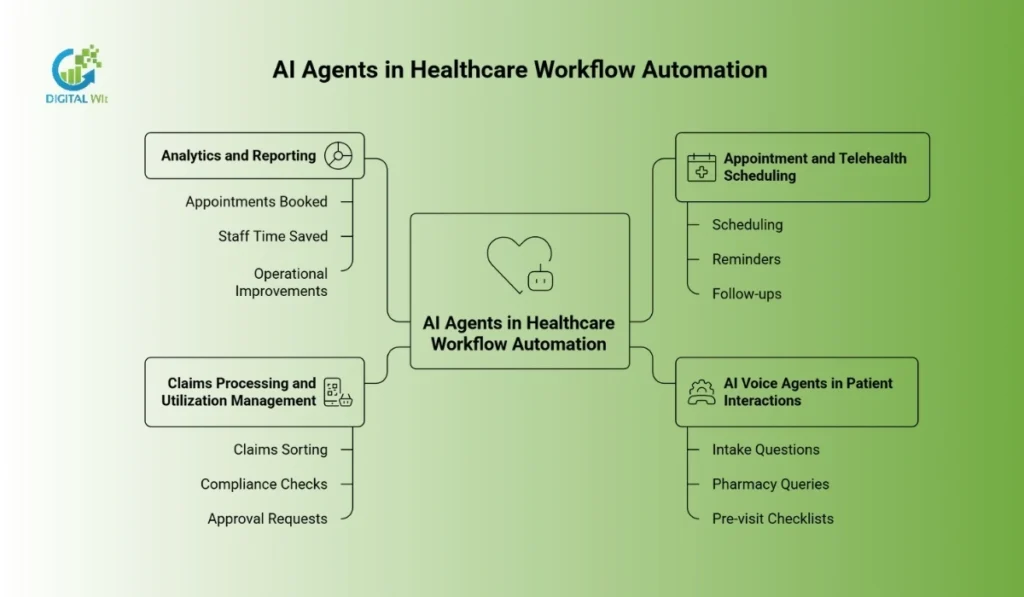
AI agents completely redesign healthcare operations, aiming to fix the massive administrative burden that wastes staff time and drives up costs. By automating repeated, multi-step tasks, agents free human staff to focus on direct patient care.
Appointment and Telehealth Scheduling
AI voice and digital agents handle the complexity of patient bookings efficiently. They manage scheduling for both in-person and telehealth appointments, including cancellations, reminders, and follow-ups.
Crucially, they link with hospital management systems, allowing them to instantly access and update schedules, patient insurance data, and preferences. This greatly reduces missed appointments and long phone queues.
AI Voice Agents in Patient Interactions
These sophisticated agents hold natural, conversational, and locally compliant patient interactions. Beyond scheduling, they handle intake questions, answer common pharmacy queries, and manage pre-visit checklists.
By smoothly talking with patients, they save significant staff time. Their success can be tracked and measured against goals for operational efficiency.
Claims Processing and Utilization Management
Agents automate the slow processes around payment. This includes automating repeated office tasks such as claims sorting, compliance checks, and approval requests.
By quickly checking documents against payer rules, agents speed up payment cycles and reduce denied claims.
Analytics and Reporting
AI agents constantly measure and report on their performance. They provide detailed data on appointments booked, staff time saved, and overall operational improvements. This data loop allows managers to constantly improve workflows.
Administrative Workflow Automation
This covers the wider set of internal tasks, including prior authorization requests, billing, and documentation. Agents ensure efficiency from start to finish, automating the fetching and sending of necessary documents while keeping to strict local data protection compliance.
Autonomous Interventions and Alerts
This highest level of autonomy means agents can take direct, safe action based on real-time data. An agent monitoring a patient’s vital signs after surgery can trigger a real-time alert to a doctor if oxygen levels suddenly drop.
In some systems, these agents can even start safe actions on their own, like adjusting a smart bed to prevent skin sores. This shows a proactive role in patient safety.
Key Benefits of AI Agents in Healthcare
The use of intelligent AI agents brings many benefits that work together across the healthcare system.
Improved Patient Engagement and Satisfaction: Virtual agents and personalized communication channels offer always-on, instant support for patients. They manage follow-ups, medication reminders, and general questions. This continuous access and personal attention lead to better adherence to care plans and happier patient experiences.
Faster, More Accurate Diagnoses: Autonomous diagnostic agents, especially those checking medical images and complex patient data, work with incredible speed and without bias. Their ability to quickly assess risk and spot early problems directly leads to earlier intervention and noticeably better patient outcomes.
Reduced Operational Costs and Staff Workload: Automating high-volume paperwork like claims processing, scheduling, and documentation removes significant manual effort. This results in major savings on operating costs and allows support staff to be moved to more important roles in direct patient care.
Easing Clinician Burnout: By taking over non-clinical duties that consume time, such as writing clinical notes via scribe agents and managing routine office processes, agents allow doctors and nurses to spend less time looking at screens. They can focus more on high-impact clinical work and meaningful patient interaction. This directly lowers a main cause of exhaustion among clinicians.
Enabling Personalized Medicine at Scale: Agents are the main tools for precision medicine. They process the huge amount of data needed from genetics to lifestyle information to deliver highly personalized treatment plans, drug doses, and therapy rules. This makes tailored care possible and accessible to many people.
Challenges and Considerations
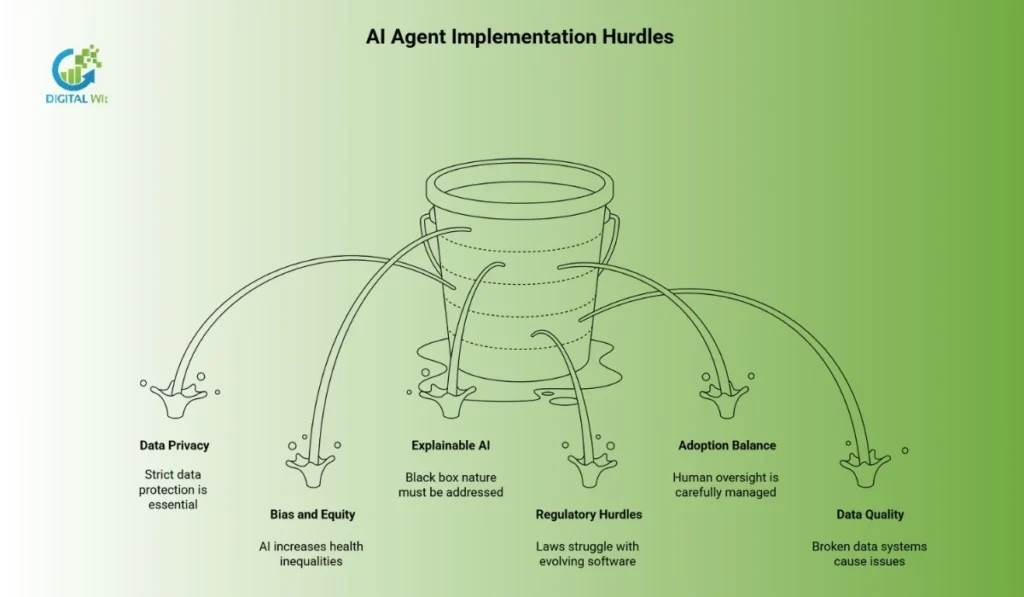
While the promise of AI agents is huge, their wide use depends on successfully handling technical, ethical, and legal challenges.
Data Privacy and Security
The foundation of any AI agent is access to private health information. Following strict data protection laws is essential. This challenge grows when data is combined from different sources, including fragmented local patient records and devices like smart sensors.
Building strong, unchangeable security systems that protect health information from breaches is critical, especially for agents that communicate on their own.
Bias and Health Equity
A serious ethical risk is that AI agents could continue or increase existing health inequalities. Given Bangladesh’s distinct rural-urban divide in access and quality of care, this is especially concerning.
If training data shows limited access to specialized care in villages, algorithms might favor diagnoses common in cities. Fixing this requires careful checks and the mandatory use of diverse datasets, including data covering various dialects and social groups, to prevent algorithmic bias and ensure fair care for everyone.
Explainable AI and Trust
For doctors to rely on AI recommendations, and for patients to accept them, the “black box” nature of deep learning systems must be addressed. Explainable AI means creating models that can clearly show the logic behind their decisions.
Ensuring transparency in AI recommendations is key for clinical responsibility, legal defense, and building trust among both medical staff and the public. A doctor must understand why an agent suggested a diagnosis before acting on it.
Regulatory Hurdles
Current laws for medical technology often struggle with software that learns and changes over time on its own. Local groups, such as the Directorate General of Health Services and related authorities, face the difficulty of adapting these rules for constantly changing medical software.
This requires new ways to monitor software after release and continuously check it to ensure it remains safe and effective.
Adoption and Human-in-the-Loop Balance
The operational challenge is often cultural. Successful integration requires widespread training for staff to change their work from manual tasks to AI-supported ones.
Building trust among doctors and nurses, who must feel confident in the agent’s reliability, is vital. The rule of keeping a “human-in-the-loop” must be carefully managed: maintaining oversight without letting unnecessary human interference slow down the agent’s efficiency or independence.
Data Quality and Integration Challenges
AI agents are only as effective as the data they use. The local healthcare system often suffers from broken, paper-based, or unconnected data systems. This leads to major interoperability issues and highly varying data quality.
Agents must be able to process, standardize, and match data from different types of sources like lab results, doctors’ notes, and time-based vital signs to ensure their decisions are accurate and reliable.
Future of AI Agents in Healthcare
The path of AI agents suggests a future where healthcare is focused on prevention, is continuous, and is highly personal.
As agents get smarter and regulations become clearer, their role will grow from simple assistance to being the main force driving clinical and operational models.
The next decade will see the full development of fully autonomous telemedicine and remote monitoring. This is essential for closing the healthcare access gap in Bangladesh. Agents will conduct first patient interviews, monitor health sensors, adjust treatment plans, and organize specialist referrals without human help in simple cases.
This capability supports predictive healthcare and preventive interventions. Here, agents automatically spot risk and step in, for example, by sending focused health advice or scheduling a preventive screening before a medical issue fully develops. The ultimate goal is to deliver hyper-personalized, real-time care that responds immediately to a person’s changing health data.
Post-Discharge Coordination
A crucial area of growth is Post-Discharge Coordination. AI agents are perfectly suited to manage the complicated time after a patient leaves the hospital or clinic.
This involves automating follow-up communication, such as confirming medication adherence and checking symptoms. Agents can quickly send learning materials, track adherence to care plans using integrated data, and only alert a human nurse if adherence or health numbers fall too low. This drastically helps lower readmission rates.
This expansion, along with continued growth of AI in behavioral health, chronic disease, and virtual assistance, promises a major change. AI agents will make sophisticated, personalized healthcare available 24/7, enabling care teams to work with maximum efficiency while focusing their human skills on what matters most: complex decisions and connecting with patients with empathy.
Final Thoughts
The rise of intelligent AI agents marks a key moment in healthcare. By moving past traditional software and adding the ability to reason and act independently, these agents can solve deep-seated problems.
From clearing massive administrative tasks and lowering operating costs to giving faster, more precise diagnoses and enabling true precision medicine, AI agents are reshaping the medical landscape.
While difficulties with data security, bias, and regulation remain, the path ahead is clear. AI agents will increasingly support human capabilities, greatly enhance operational efficiency, and fundamentally transform patient care. They’re bringing about a time of continuous, proactive, and highly personalized health management.
For healthcare organizations in Bangladesh looking to navigate this digital transformation and communicate these innovations effectively, partnering with experts is essential. Digital Wit, the best digital marketing agency in Bangladesh, specializes in helping healthcare brands tell their story and reach the right audience in this rapidly evolving landscape.
FAQ
How much AI is being used in healthcare?
AI is increasingly integrated across hospitals, clinics, telehealth, diagnostics, and administrative processes, with adoption expected to grow significantly.
Which tasks can AI agents automate safely?
Appointment scheduling, patient reminders, claims processing, prior authorizations, documentation, repetitive administrative tasks, predictive alerts, and telehealth follow-ups.
How can AI detect fraud efficiently?
By analyzing billing patterns, identifying anomalies, cross-checking claims against historical data, and monitoring compliance automatically.
Where is data quality blocking AI adoption?
Poor EHR data quality, incomplete patient histories, incompatible legacy systems, and unstructured or inconsistent data prevent effective AI deployment.
Which AI voice platforms provide natural, HIPAA-compliant patient interactions?
Platforms using advanced natural language processing with HIPAA compliance capabilities, capable of handling bookings, reminders, follow-ups, and EHR integration.