Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved. It moved from a theoretical discipline into a driving force behind digital transformation.
From customer support bots to self-driving vehicles, AI systems are taking on autonomous roles. These roles were once managed by humans. Yet, beneath these varied applications lies one fundamental concept: the AI agent.
An AI agent is not just a piece of software. It’s an intelligent entity. It can perceive its environment. It reasons through available data. It acts with purpose.
These agents differ by complexity. Some follow simple, rule-based instructions. Others learn from experience and adapt over time.
Key Takeways
- AI agents are autonomous systems that perceive their environment, make decisions, and act toward achieving defined goals
- The seven foundational types of AI agents form a hierarchy of intelligence: from basic reflex-based responses to adaptive, learning-driven, and collaborative systems
- Modern industries, including marketing, finance, logistics, and customer service in Bangladesh, are incorporating semi-autonomous and learning agents to improve efficiency and decision-making
- Each agent type offers unique strengths: reflex agents excel in stable environments, while learning and hierarchical agents thrive in dynamic, unpredictable systems
- The convergence of machine learning, natural language processing, and multi-agent architectures is shaping the next generation of enterprise AI
- Understanding these agent types helps businesses, developers, and decision-makers choose the right model for their automation and intelligence goals
AI in Bangladesh
Globally, the AI landscape continues to expand. Bangladesh is no exception.
Forward-looking businesses in Dhaka, Chattogram, and Rajshahi are integrating AI-powered automation. They use it in marketing analytics, logistics, and fintech solutions.
This movement signals a growing awareness. Intelligent agents can augment human decision-making. They can scale productivity far beyond manual operations.
We’ll explore the seven main types of AI agents. We’ll cover reflex-based systems to hierarchical and multi-agent frameworks.
You’ll understand how they operate. You’ll learn where they excel. You’ll see how they’re shaping the future of intelligent automation.
1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents operate based on direct, rule-based responses.
They perceive an environmental condition. They instantly act using if-then logic. They have no memory or awareness of past events.
This simplicity makes them efficient for predictable systems. They work well in fully observable systems. Every situation has a clear, predefined action.
How They Work
When the environment matches a particular condition, the agent performs a corresponding action.
For instance, a thermostat switching off when a set temperature is reached. This is a classic example of a simple reflex system.
Strengths
- Fast and lightweight decision-making
- Easy to implement and maintain
- High reliability in stable environments
Limitations
- Cannot handle uncertainty or partial observability
- Fails in dynamic environments requiring historical context or prediction
In Bangladesh, simple reflex agents are often used in basic process automation tools. These include website chat widgets, traffic signal control systems, or rule-based marketing responses.
They serve as the foundation for more advanced agent evolution.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-based reflex agents build upon the simplicity of reflex agents. They maintain an internal representation of the world. This is a model of the environment that helps interpret unseen conditions.
These agents make decisions based on more than just current input. They also use past states and inferred knowledge about the system they interact with.
How They Work
Each time the environment changes, the agent updates its internal model. Then it decides what action best aligns with its understanding of reality.
For example, a robot vacuum that remembers the layout of a room. It avoids previously cleaned areas. This operates as a model-based reflex agent.
Strengths
- Handles partially observable environments
- Can infer missing data or unseen states
- More adaptable than simple reflex agents
Limitations
- Requires more computational power
- May become inaccurate if the model is not updated or trained properly
In sectors like logistics or real estate analytics in Bangladesh, model-based agents assist with route optimization and occupancy predictions. They work where conditions are partially observable but predictable patterns exist.
3. Goal-Based Agents
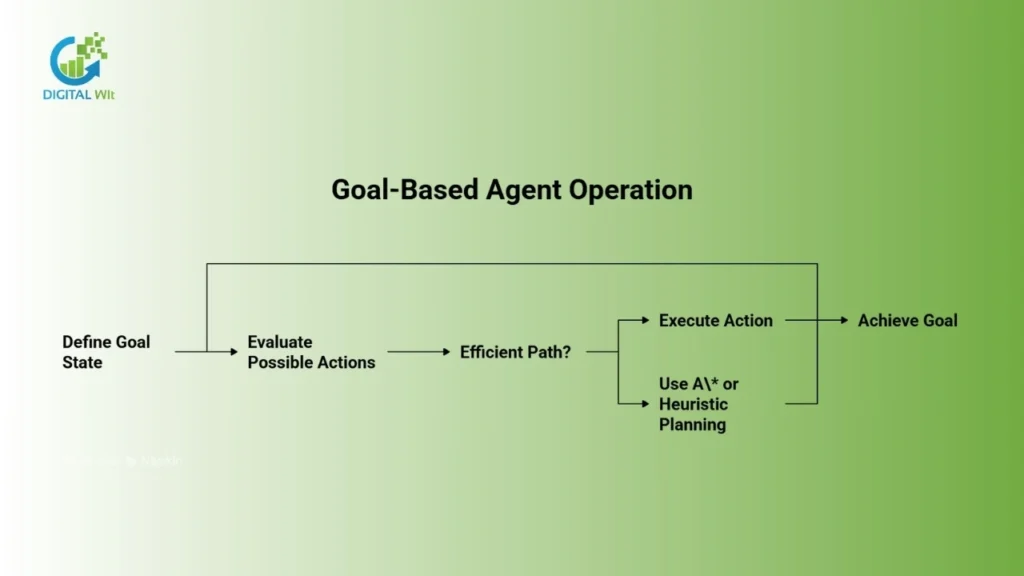
Goal-based agents are designed to act with a specific objective in mind.
They don’t just react to the environment. They plan and reason toward a desired outcome. They use search and optimization strategies.
How They Work
The agent defines a goal state. It evaluates possible actions that could achieve it.
It uses algorithms such as A* or heuristic-based planning. This helps it decide the most efficient path.
An example is a GPS navigation system. It continuously calculates the optimal route to a destination.
Strengths
- Purpose-driven and proactive
- Capable of long-term planning
- Effective in dynamic, goal-oriented tasks
Limitations
- Computationally expensive for complex goals
- Requires clear goal formulation and accurate state modeling
In Bangladesh’s growing e-commerce and fintech industries, goal-based agents assist in fraud detection, loan evaluation, and delivery scheduling.
The system must continuously optimize to meet business objectives.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents introduce a layer of sophistication. They incorporate preferences or utility functions that measure satisfaction.
Instead of simply achieving a goal, they evaluate which action yields the highest overall value. They compare competing options.
How They Work
The agent quantifies potential outcomes. It selects the one with the best trade-off between factors. These factors include cost, efficiency, and safety.
A self-driving car choosing between routes is an example. It balances speed, traffic, and fuel efficiency. This embodies utility-based reasoning.
Strengths
- Supports complex decision-making
- Balances multiple criteria
- Works well under uncertainty
Limitations
- Designing accurate utility functions is challenging
- Computation can be intensive in real-time environments
Utility-based logic is finding its way into digital marketing campaign optimization. It’s also used in resource allocation systems in Bangladesh.
This helps businesses choose the most cost-effective strategy. They maintain engagement and performance balance.
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents are at the heart of modern AI progress.
These systems continuously learn from experience. They improve their performance over time. They use feedback loops, data analysis, and adaptation.
How They Work
A learning agent includes:
A learning element that refines behavior based on feedback
A critic that evaluates outcomes and guides learning
A performance element that carries out learned strategies
This architecture allows the agent to handle new, unseen situations effectively.
Strengths
- Adaptable and self-improving
- Performs well in uncertain and evolving environments
- Core of machine learning and reinforcement learning applications
Limitations
- Training requires large datasets
- May exhibit unpredictable behavior during exploration phases
Bangladesh’s banking and customer service sectors are beginning to explore learning agents. They use them in chatbots, fraud monitoring, and customer recommendation systems.
They combine local data with global AI frameworks for smarter automation.
6. Hierarchical Agents
Hierarchical agents organize intelligence in layers. Each level manages a different level of abstraction or task complexity.
This layered approach enables systems to scale, delegate, and manage complex operations efficiently.
How They Work
High-level agents define strategic goals. Lower-level agents execute specific, tactical actions.
For example, in a smart manufacturing plant, a top-level planner may decide production targets. Lower-level robotic agents execute assembly operations.
Strengths
- High scalability and modularity
- Clear division of labor between strategic and operational functions
- Robustness in multi-step, complex workflows
Limitations
- Potential communication bottlenecks
- Requires coordination and synchronization across layers
As Bangladesh’s industrial automation and supply chain technologies evolve, hierarchical architectures can enhance decision layering.
This applies to warehouse management systems to predictive maintenance scheduling.
7. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Multi-agent systems represent collaborative intelligence. They are networks of multiple agents interacting, negotiating, and coordinating to achieve shared or competing goals.
How They Work
Each agent in the system may have unique goals, knowledge, or capabilities.
Through communication and coordination, they collectively solve distributed problems. These include load balancing, resource sharing, or complex simulations.
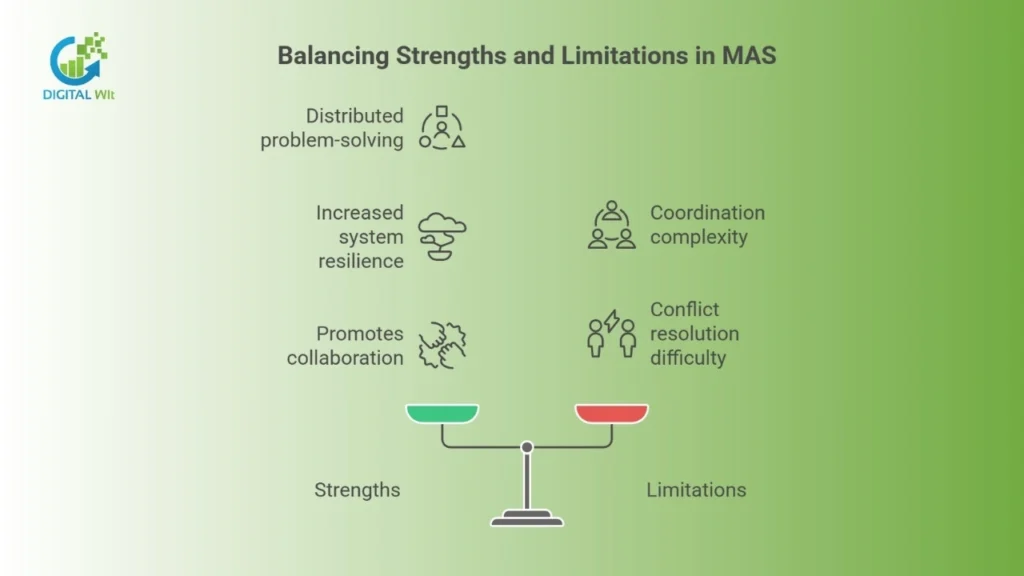
Strengths
- Enables distributed problem-solving
- Increases system resilience
- Promotes collaboration and parallelism
Limitations
- Coordination complexity increases with scale
- Conflict resolution between agents can be difficult
Multi-agent models have strong potential in Bangladesh’s logistics, traffic management, and energy systems.
Distributed coordination among vehicles, warehouses, or grids can optimize national-scale efficiency.
Conclusion
AI agents are evolving. They’re moving from code-based responders to autonomous collaborators. They drive innovation across industries.
Businesses that understand their mechanics can deploy smarter, scalable automation. This isn’t just to cut costs. It’s to unlock strategic creativity and insight.
For Bangladesh’s emerging AI economy, the lesson is clear. Start simple. Evolve strategically. Align agent design with local challenges.
Focus on areas from customer experience to supply chain efficiency.
For forward-thinking teams, it’s not about replacing humans. It’s about amplifying intelligence with intention.
Learn how your brand can harness AI automation in Digital Wit AI Solutions.