Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of modern technology, driving automation, optimization, and smarter decision-making across industries. Central to this innovation are intelligent agentsAutonomous systems capable of perceiving their environment, processing information, and taking action toward achieving specific goals often incorporate generative AI.
Understanding how an intelligent AI agent can interact with its environment effectively works is essential for businesses, researchers, and technology enthusiasts, as these agents form the backbone of AI solutions in areas ranging from customer support to autonomous vehicles.

Key Takeaways:
- Intelligent agents are smart AI programs that learn and make decisions on their own.
- AI agents help businesses by doing tasks, analyzing data, and giving useful advice.
- Intelligent AI agents see what is happening, think about it, and take action to reach goals.
- From virtual helpers to self-driving cars, intelligent agents make work easier and faster.
- Intelligent agents use AI to handle tasks, learn from data, and give helpful results.
Understanding Intelligent Agents
Intelligent agents are autonomous entities that interact with their environment to accomplish specific objectives. These agents gather data, process information, and make decisions independently, without constant human intervention. They form the core of AI applications that rely on automation, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making.
The importance of intelligent agents in modern AI systems spans industries and applications. From AI-powered virtual assistants to robotic process automation, these agents enhance operational efficiency, reduce errors, and provide scalable solutions for complex tasks.
Understanding the An intelligent agent in AI can learn from its interactions to make better decisions based on data. concept is crucial to leveraging these systems effectively in both enterprise and consumer-facing applications.
Intelligent Agents Concepts and Key Characteristics
To fully understand intelligent agents, it is essential to explore the key characteristics that define how they operate. These features include autonomy, perception, action, rationality, and the ability to react and proactively plan for future scenarios.
Autonomy allows agents to function independently, executing tasks without constant human oversight. Perception enables intelligent agents to gather data from their environment using sensors or digital feeds, while action allows them to influence their surroundings.
Rationality ensures that agents make logical and goal-oriented decisions, and reactivity combined with proactivity allows them to respond to immediate changes while planning for long-term objectives.
Collectively, these characteristics enable intelligent agents to solve problems, automate repetitive tasks, and optimize workflows in complex and dynamic environments.
Types of Environments
Intelligent agents operate in a wide variety of environments, each requiring specific strategies and design considerations. Fully observable environments provide complete information for decision-making, whereas partially observable environments force agents to infer missing data and anticipate potential outcomes.
Environments can also be deterministic, where outcomes are predictable, or stochastic, where uncertainty affects decision-making. They may be episodic, with independent tasks, or sequential, where actions impact future states.
Agents may encounter static conditions that do not change or dynamic ones that require real-time responses. Additionally, environments may be discrete, with clearly defined states, or continuous, requiring smooth adaptation.
Understanding the environment type is crucial for designing intelligent agents that perform reliably in real-world conditions.
Applications of Intelligent Agents
Intelligent agents have transformative applications across business functions and industries, delivering automation, efficiency, and intelligent insights.
Intelligent Agents Across Business Functions
Intelligent agents improve efficiency in sales, marketing, customer service, finance, insurance, pharma, manufacturing, transportation, retail, and education. Sales AI agents Agents can provide management of lead scoring and pipelines, while also optimizing marketing strategies.
Marketing AI agents can leverage generative AI to create personalized campaigns. Agents can process data to personalize campaigns and improve conversions effectively. Customer service AI agents use AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to resolve queries efficiently. In finance, intelligent agents assist with fraud detection and automated reporting.
Insurance AI agents can provide personalized policy recommendations based on user data. streamline claims processing, while Pharma AI agents can process vast amounts of data to improve drug development and patient outcomes, showcasing examples of intelligent agents in healthcare. accelerate drug discovery. Manufacturing, transportation, retail, and education sectors benefit from intelligent agents’ ability to optimize workflows and improve operational efficiency, especially through model-based agents.
Intelligent Agents Across Industries
In addition to business functions, intelligent agents are embedded across industries, allowing them to work with other agents effectively. Virtual assistants are a popular use case for intelligent agents in artificial intelligence, as these agents can provide enhanced user experience through personalized interactions. like Siri and Alexa improve everyday task management, while autonomous vehicles rely on agents for navigation and safety.
Recommender systems are examples of intelligent agents that enhance user experiences by providing personalized suggestions. personalize user experiences in media and retail, and robotic agents execute complex physical tasks in industrial settings. Financial trading agents optimize investment strategies, and healthcare agents assist in patient monitoring and diagnostics. AI agents also play crucial roles in gaming, simulations, and government security operations.
Intelligent Agents Examples Across Departments
Different departments within organizations benefit from specialized AI agents. Customer service automation agents Enhance response speed and quality, while intelligent agents collect data to improve performance. sales process automation agents manage leads and reporting. Business process automation agents reduce manual work by handling repetitive tasks.
Development and technical agents in artificial intelligence. assist coding, testing, and deployment workflows, while Analysis and intelligence agents can enhance user interactions significantly. aggregate data and provide actionable insights to improve decision-making.
Multi-Agent Systems
Multi-agent systems involve multiple intelligent agents interacting to achieve goals collectively, requiring effective communication and coordination.
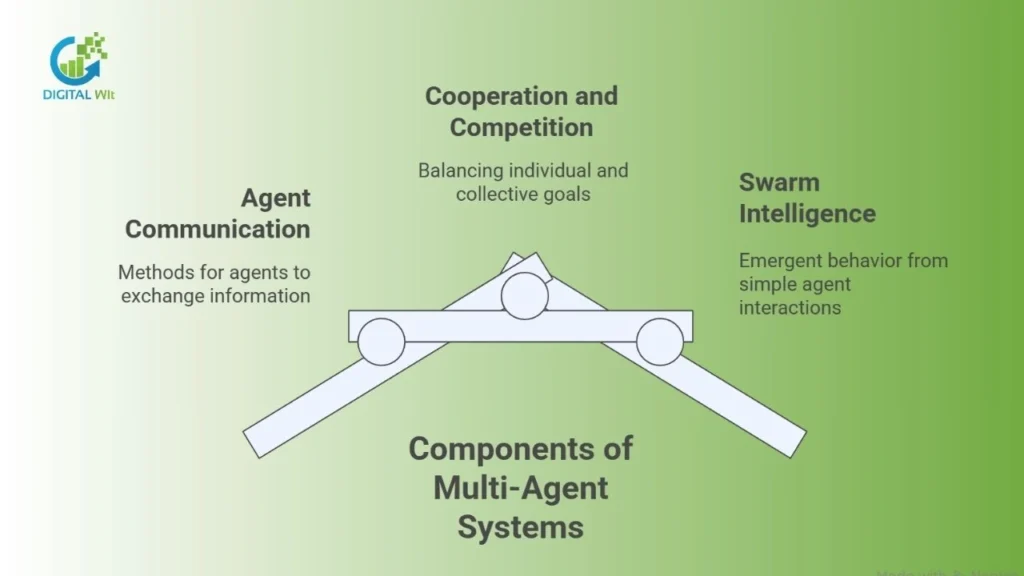
Agent Communication
In multi-agent environments, agents exchange information through structured languages, negotiation protocols, and coordination methods. Effective communication ensures seamless collaboration, task allocation, and conflict resolution, allowing the system to function efficiently as a whole.
Cooperation and Competition
Agents often balance cooperation and competition.To optimize both individual and collective objectives, agents require advanced algorithms and frameworks. Techniques such as collaborative problem-solving, resource allocation, and game theory guide agents in achieving shared goals while maximizing efficiency using intelligent agents.
Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence emerges when simple agents interact according to basic rules, resulting in complex, adaptive, and emergent behavior. This approach is widely used in optimization, robotics, and network management, allowing multiple agents to work together efficiently and adaptively.
Technologies Enabling Intelligent Agents
Modern intelligent agents rely on technologies like machine learning, NLP, computer vision, and knowledge representation to function autonomously. These technologies allow agents to learn from data, understand human language, perceive their environment, and make informed decisions efficiently.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine learning and deep learning equip intelligent agents with the ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions. Techniques like reinforcement learning, neural networks, and supervised/unsupervised learning enable agents to learn from experience and operate independently.
Natural Language Processing
NLP allows intelligent agents to interpret, understand, and generate human language. This capability supports AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are examples of using intelligent agents to enhance user experience., and other conversational agents, enabling them to respond accurately to user queries and provide actionable information.
Computer Vision
Computer vision enables agents to perceive and understand visual information. Applications include image recognition, object detection, and real-time environment monitoring are essential for AI assistants., which are essential for autonomous vehicles, security, and robotic operations.
Knowledge Representation
Agents rely on knowledge representation to store, organize, and reason with information. Ontologies, semantic networks, and reasoning systems help agents make informed decisions, learn from past experiences, and operate effectively in complex, dynamic environments.
Challenges and Limitations
Developing intelligent agents comes with ethical, technical, and interaction challenges. Ensuring fairness, handling complex computations, and building human trust are key to creating safe and transparent AI systems that work effectively in real-world settings.
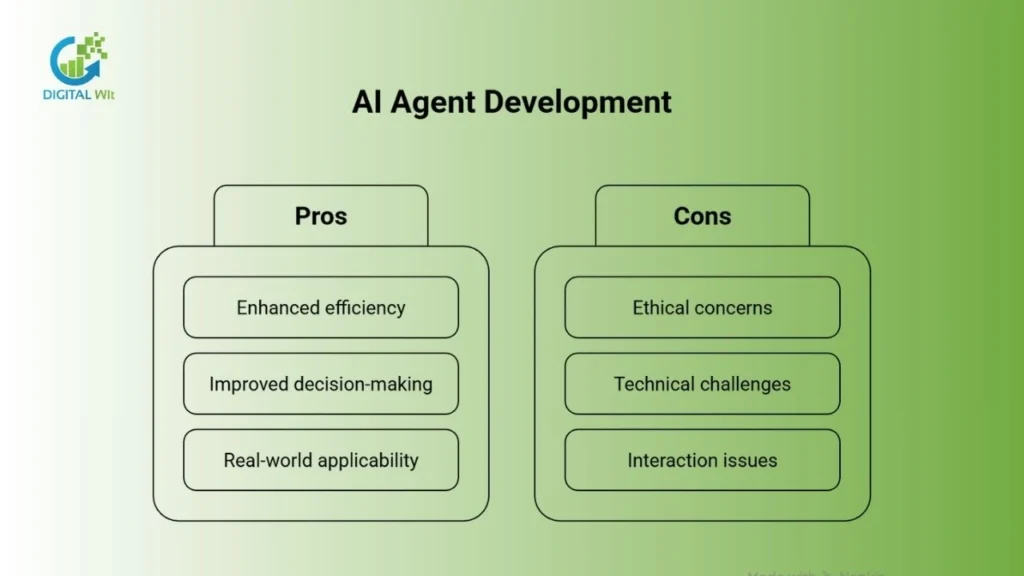
Ethical Considerations
The rise of intelligent agents raises ethical concerns such as bias, accountability, transparency, and explainability. Ensuring fairness, protecting data privacy, and building trust are essential for the responsible deployment of AI agents.
Technical Challenges
Agents face Addressing technical challenges is crucial for developing effective types of agents in AI. Challenges include scalability, computational resource demands, handling uncertainty, and ensuring safe operation for autonomous AI agents. Addressing these challenges is critical for deploying reliable and robust agentic AI systems.
Human-Agent Interaction
Successful integration of intelligent agents depends on building trust, designing intuitive interfaces, and promoting user acceptance. Agents must communicate effectively, provide reasoning for their decisions, and operate in a way that complements human agents and AI assistants.
Future Directions of Intelligent AI
The future of intelligent agents lies in advancements toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and the integration of emerging technologies. Innovations like quantum computing, edge AI, and IoT will make future agents more adaptable, human-like, and capable of real-time decision-making.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
AGI represents the evolution of AI toward general-purpose intelligent systems can utilize advanced AI to optimize their functions. Intelligent agents are capable of reasoning, learning, and problem-solving across domains, which is essential for building AI agents. AGI will allow intelligent agents to adapt to novel situations and make decisions with human-like flexibility.
Emerging Trends
Technologies such as agent programs and machine learning are crucial for developing intelligent agents. edge computing, quantum computing, and IoT integration are enhancing intelligent agents’ speed, accuracy, and adaptability using advanced AI. These trends allow agents to process information locally, handle large amounts of data, and interact seamlessly with connected devices using AI agents often.
Societal Impact
The widespread adoption of intelligent agents will transform the workforce, create new job categories, and redefine human-agent interactions, particularly through various types of intelligent agents. Intelligent agents can increase productivity, reduce manual work, and enable humans to focus on strategic, creative, and high-value tasks.
At Digital Wit, we specialize in providing advanced AI agent solutions that help businesses automate workflows, analyze data, and deliver smarter outcomes. Whether you need virtual assistants, intelligent automation, or AI-powered decision-making tools, Digital Wit empowers your organization to unlock the full potential of intelligent AI agents.
Explore how Digital Wit can transform your business with intelligent agent solutions and take your AI strategy to the next level.
FAQs
What is an example of an Intelligent AI agent?
Siri, Alexa, and autonomous vehicles exemplify intelligent agents.
How do Intelligent AI agents work?
By perceiving environments, analyzing information, and taking actions aligned with specific goals.
How to create an AI agent?
Through AI models, agent frameworks, and decision-making algorithms, intelligent agents work efficiently to solve complex problems.
What are the functions of an AI agent?
Automating tasks, decision-making, learning from data, and interacting with humans.
What are the types of AI agents?
Simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents.