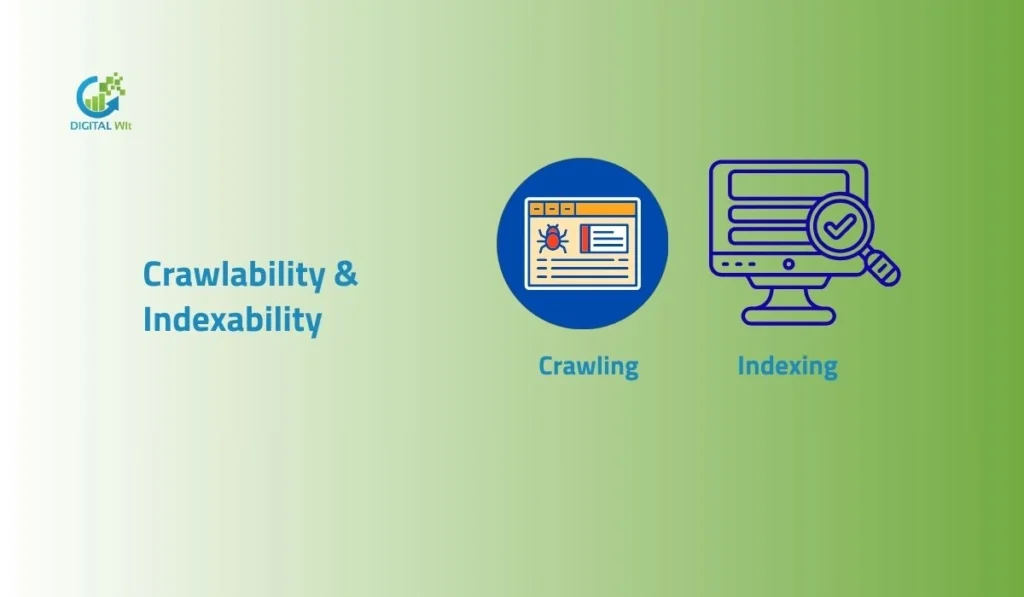
You have a great website with good content. But no one finds it on Google. Why?
Search engines cannot see your pages. This happens because of crawlability and indexability problems. Get more inside from Digital Wit like what crawlability and indexability mean. It shows the difference between them. Why they matter for SEO and organic traffic.
Good crawlability lets Googlebot visit your pages. Good indexability lets Google add them to search results. Without these, your site stays invisible.
What Is Crawlability?
Crawlability is how easily search engines can access and read your website pages. Googlebot, Bingbot, and other web crawlers follow links and explore your site to find content. A clear site structure, proper internal linking, and fast server response help crawlers move smoothly.
Crawl budget is the limit of pages a bot can visit in a time, and crawl depth shows how many clicks it takes to reach a page. Crawl paths guide bots through your website. If your pages are not crawled, they cannot appear in search results, which means no organic traffic for your site.
What Is Indexability?
Indexability is the ability of search engines to store your pages in their search index. After crawling and rendering, bots decide which pages to include based on content quality and technical signals. Pages can be indexed, crawled but not indexed, discovered but not indexed, or blocked.
Only indexed pages can appear in search results and get organic traffic. Without proper indexability, your website content cannot rank, no matter how good it is. Ensuring pages are indexable is essential for search visibility and for users to find your content online.
How do Search Engines Handle Crawlability and Indexability?
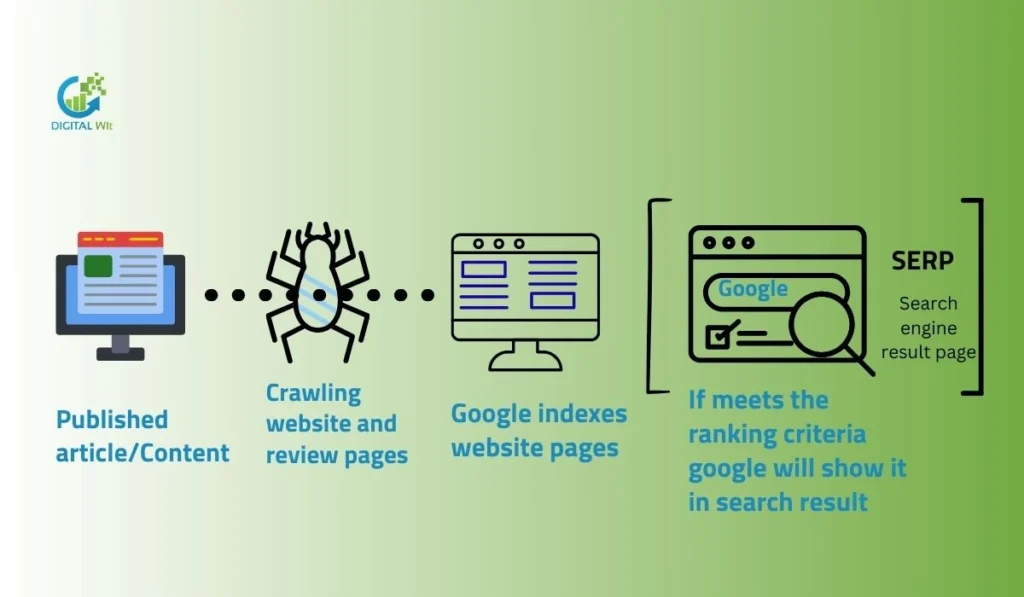
Search engines use bots like Googlebot to find and visit web pages.They follow links, read XML sitemaps, and check server responses to crawl sites.After crawling, they decide if pages are good enough to add to the search index for showing in results.
Overview of Technical SEO and the Search Engine Process
Technical SEO helps search engines understand your website. The process starts with discovery, then crawling, rendering, indexing, and finally ranking. Each step ensures your pages can appear in search results.
The Role of Search Engine Bots
Search engine bots like Googlebot and Bingbot visit websites to read content. They follow links, check pages, and send information back to the search index. Without bots, pages cannot appear in search results.
How Web Crawlers Access and Discover Pages
Web crawlers find pages through internal links, external backlinks, and XML sitemaps. They analyze the website structure and follow paths to reach all important pages.
Introduction to Discovery
Discovery starts with links from other websites, previously crawled URLs, and submitted XML sitemaps. These starting points guide crawlers to new or updated content.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of Crawling and Indexing
A page is first discovered, then crawled, rendered, and finally indexed. Crawling checks the page content, rendering interprets scripts, and indexing adds the page to the search index.
Implementing proper On-Page SEO Techniques ensures that your pages are structured, optimized, and easy for search engine bots to understand, improving both crawlability and indexability.
Crawlability Indicators
Crawl stats, server logs, and SEO tools show how well search engines crawl your website. Monitoring these helps identify blocked pages or crawl errors that limit visibility.
Crawlability vs. Indexability
Crawlability means search engine bots like Googlebot can reach and visit your pages easily.Indexability means those bots can understand and add your pages to the search index for showing in results.
The big difference is: crawlability is about access, while indexability is about inclusion in search.
Crawlability = Access and Discovery
Crawlability is how easily search engine bots can access and explore your website. If your pages are hard to reach, search engines may never see them. Proper internal linking, site structure, and XML sitemaps help bots discover your content. A site with low crawlability will have hidden pages and lost opportunities for search visibility.
Indexability = Inclusion in Search Results
Indexability is about whether a page can be stored in a search engine’s index. Even if a page is crawled, it may not appear in search results due to issues like noindex tags, duplicate content, or low-quality content. Indexed pages are the only ones that can rank and bring organic traffic.
How They Interact: Crawlability as Foundation for Indexability
Crawlability comes first. Without bots accessing your pages, indexability cannot happen. A page must be discovered, crawled, and then analyzed before it can be included in search results.
Visual Comparison (Suggested Table/Diagram)
A simple table can show crawlability on one side and indexability on the other. It helps readers quickly understand that one is about access and the other is about inclusion.
Real-World Examples and Common Misinterpretations
Many website owners confuse crawlability with indexability. A page may be crawled but not indexed due to technical errors. Fixing crawlability alone does not guarantee indexing.
How Crawlability & Indexability Impact SEO
Good crawlability and indexability help your pages show up in search results. They bring more organic traffic and better rankings to your site. If these are poor, your content stays hidden, and you lose visitors and sales. To understand how to optimize your website effectively, you can see how we work as the leading SEO agency in Bangladesh for practical strategies and guidance.
Impact on Search Visibility, Rankings, and Organic Traffic
Crawlability and indexability directly affect how search engines see your website. If your pages are not crawled or indexed, they will not appear in search results. This lowers search visibility and reduces organic traffic. Websites with proper crawlability and indexability often rank higher because search engines can access and evaluate content efficiently.
Consequences of Issues
When crawlability or indexability is poor, search engines waste crawl budgets on unimportant pages. Important pages may remain invisible. This leads to lost opportunities for attracting visitors and generating leads.
Benefits of Optimization for Small and Large Sites
Optimizing crawlability and indexability helps all websites. Small sites gain better visibility quickly, while large sites ensure search engines find key pages. This improves rankings, traffic, and overall SEO performance.
Using a Technical SEO Audit Checklist can help you systematically identify and fix issues affecting crawlability and indexability, ensuring your site is fully optimized for search engines
Understanding Crawl Budget
Crawl budget is the number of pages Googlebot can crawl on your site in a short time.It depends on your site size, speed, and how popular your pages are.Small sites do not worry much, but large sites need to manage it well to avoid waste.
What Is Crawl Budget and Crawl Efficiency?
Crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine can crawl on your website. Crawl efficiency means how well crawlers use this budget. If pages are easy to reach, crawlers visit more pages quickly. This helps search engines find and index your content faster.
Factors Affecting Crawl Budget
Site size affects how many pages can be crawled. Healthy websites with strong authority are crawled more often. Frequently updated pages get higher priority. Slow or broken pages waste crawl budget. Proper structure and internal links help crawlers move efficiently across the website.
When Crawl Budget Matters
Large websites need careful crawl budget management. Small sites usually do not face limits. If crawlers waste a budget on unnecessary pages, important pages may be missed. Monitoring and optimizing crawl paths ensures the most valuable pages are indexed and visible in search results.
How to Check and Monitor Crawl Budget
You can check the crawl budget using Google Search Console. Crawl stats and URL inspection reports show which pages are crawled. Logs from server files help identify issues. Regular monitoring helps ensure search engines index the right pages on time.
Key Factors Affecting Crawlability & Indexability
Many things affect crawlability and indexability of your website. Site structure, internal linking, robots.txt, and XML sitemaps play big roles. Page speed, mobile-friendliness, content quality, and JavaScript rendering also matter a lot.
Site Architecture, URL Structure, and Navigation
The structure of your website affects how web crawlers find and crawl pages. Clear navigation menus, category pages, and homepage links help crawlers reach every page. Simple and descriptive URLs also make it easier for search engines to understand your site.
Internal Linking, Link Depth, and Orphan Pages
Internal linking connects pages and guides crawlers through your site. Deep pages without links, called orphan pages, may not be discovered. Proper link depth ensures crawlers spend time on important pages first.
Robots.txt File (User-agent, Allow/Disallow Directives)
Robots.txt tells crawlers which pages they can or cannot access. Incorrect settings may block important pages from being crawled. Always check user-agent, allow, and disallow directives carefully.
Discovery Signals for Search Engines
Search engines need ways to find and understand your website. Discovery signals help bots access pages and decide which content to crawl and index. Proper signals improve visibility in search results.
XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all important pages on your website. You should include pages that matter and avoid duplicate or low-value pages. Submitting it to Google helps search engines find new content faster.
Backlinks and External Discovery
Backlinks are links from other websites to your site. They show search engines that your content is important. High-quality backlinks help crawlers discover more pages and improve indexability.
HTML Sitemaps and Navigation Menus
HTML sitemaps and menus guide users and search engines through your site. They reduce orphan pages and make it easy for bots to reach all pages. Adding Schema Markup on key pages further helps search engines understand your content and can enhance rich results. Good navigation improves both crawling and indexing.
Common Crawlability Issues and Fixes
Robots.txt Problems
Many websites block important pages by mistake using robots.txt. Wrong syntax or blocking CSS and JavaScript can stop crawlers from accessing content. You should check robots.txt regularly and use testing tools to fix errors.
Poor Internal Linking and Orphan Pages
Pages without links or with weak internal linking are hard for bots to find. Orphan pages stay undiscovered and reduce crawl efficiency. Adding proper links from menus and other pages can solve this problem.
Broken Links, 404 Errors, and Redirect Chains
Broken links and long redirect chains waste crawl budgets. Pages showing 404 errors prevent search engines from crawling your site efficiently. Fix broken links and simplify redirects to improve crawlability.
Common Indexability Issues and Fixes
Incorrect Noindex Tags
Some pages have noindex tags. This stops search engines from adding pages to the index. Remove unnecessary noindex tags to make pages indexable.
Canonical Conflicts and Duplicate Content
Duplicate content or wrong canonical tags confuse search engines. Pages may not appear in search results. Fix canonical tags and remove duplicate content for better indexability.
Thin or Low-Quality Content
Pages with very little useful content may not get indexed. Improving content quality and adding original information helps pages appear in search results.
How to Check and Monitor Crawlability & Indexability
Using Google Search Console
You can check your website’s crawlability and indexability using Google Search Console. The Coverage report shows which pages are indexed and which have errors. Crawl Stats help you understand how often Googlebot visits your site. The URL Inspection tool lets you check a specific page’s index status. The Sitemaps report helps ensure all important pages are submitted correctly.
Manual Methods
You can use the site: operator to see which pages are indexed. Viewing the page source helps check meta tags and robots directives. Browser tools show how pages load and render content.
Log File Analysis
Log files show which pages are crawled and how often. Crawl monitoring helps find blocked or low-priority pages. You can use these reports to fix errors and improve index coverage.
Best Practices and Practical Techniques to Improve
Optimize Site Structure and Internal Linking
A clean site structure helps search engines find pages easily. Organize pages into categories and subpages so links are clear. Use internal linking to connect related pages and avoid orphan pages. Proper linking improves crawl efficiency and helps important pages get indexed faster.
Create, Submit, and Maintain XML Sitemaps
An XML sitemap shows search engines all pages on your website. Create a sitemap including important pages only. Submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. Keep updating the sitemap whenever new pages are added or removed.
Review and Optimize Robots.txt
Check your robots.txt file to avoid accidentally blocking important pages. Use allow and disallow directives carefully. Make sure search engine bots can access pages needed for indexing.
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Crawl Budget Optimization for Large/E-commerce Sites
Large websites or online stores need careful crawl budget management. You should prioritize important pages and reduce low-value pages. Proper pagination and managing faceted navigation help search engines crawl efficiently. This ensures Googlebot and other bots reach key pages quickly and reduces wasted crawling.
JavaScript Rendering Best Practices
JavaScript can block content from being seen by crawlers. Using server-side rendering helps search engines read content fully. This improves both crawlability and indexability. Test your pages to ensure crawlers can access all content.
International SEO
For multi-language sites, hreflang tags guide search engines to the correct version. Clear multi-language site structure avoids confusion. This ensures users in different countries see relevant content.
Recommended Tools
Google Search Console and Related Free Tools
Google Search Console helps you check crawl errors and index coverage. You can see which pages are indexed and monitor technical SEO issues. Bing Webmaster, Mobile-Friendly Test, and Rich Results Test provide additional insights to ensure your website works well for users and search engines.
Third-Party Tools
Screaming Frog and Ahrefs help find broken links, duplicate content, and other crawlability issues. Log file analyzers and XML sitemap generators make it easier to manage large sites. These tools improve site structure, monitor performance, and support better indexability in search results.
Ongoing Maintenance and Long-Term Best Practices
Regular technical SEO audits help you find and fix issues that may block search engines from crawling or indexing your pages. By checking your website often, you can prevent small problems from affecting search visibility.
Scheduled log reviews and content updates keep your website fresh and crawlable. Reviewing server logs shows how search engine bots interact with your site, and updating content improves page relevance.
Maintaining clean architecture ensures all pages are easy to find. Following SEO guidelines and updating your site structure regularly helps search engines crawl and index your website efficiently.
FAQs
What is the difference between crawling and indexing in SEO?
Crawling is when search engine bots visit your website to read pages. Indexing happens after crawling when the content is stored in the search engine’s database. Crawled pages are not always indexed, but only indexed pages can appear in search results.
What Is Crawlability in SEO? How to Make Sure Google Can Access and Understand Your Site
Crawlability means Google can visit and read your pages. Use proper internal linking, XML sitemaps, and fix robots.txt rules. Ensure pages load quickly and have clear URLs. These steps help search engines crawl and understand your content correctly.
What are crawlability and indexability? How do they affect SEO?
Crawlability is when search engines can access pages, and indexability is when pages are stored in the search index. Both are needed to appear in search results.
How do crawlability and indexability affect websites and SEO?
If pages cannot be crawled or indexed, they won’t show in search results, which lowers traffic and visibility, even for good content.
What is crawlability and indexability in SEO and its importance?
Crawlability lets bots find your pages, and indexability lets them appear in search. Together, they are crucial for higher rankings and more organic traffic.
Conclusion
In summary, crawlability and indexability are key for your website to appear in search results. Follow best practices, fix errors, and monitor regularly. Take action with audits and updates. Experts at Digital Wit provide guidance to help maintain visibility, attract organic traffic, and achieve long-term SEO success for your site.