The modern enterprise demands efficiency: automated workflows, scaled content creation, and data-driven decisions powered by AI.
Yet, selecting the right technology is the most common pitfall. Deploying the wrong tool can stall projects, deplete resources, and compromise executive confidence in your AI strategy. Achieving measurable ROI requires precise technical understanding.
This analysis provides a definitive breakdown of the core technologies driving modern automation: AI Agents and Large Language Models (LLMs). We detail their unique operational profiles, define their distinct capabilities, and establish a framework for strategic integration.
By mastering the fundamental differences – where Agents handle action and autonomy and LLMs provide scalable language intelligence – your organization can achieve end-to-end automation, maximize productivity, and deploy a robust, competitive AI infrastructure.

Key Takeaways
- AI Agents automate workflows and act independently
- LLMs generate high-quality, scalable text outputs
- Combining both boosts efficiency, ROI, and consistency
- Agents learn from results; LLMs learn from text patterns
- Integration enables end-to-end automation across business tasks
Why You Should Care About These Differences
Businesses that don’t understand the difference waste resources. Picking the wrong tool can slow processes. It reduces efficiency. It prevents automation gains.
Understanding these differences helps companies deploy the right technology for the right job. This ensures faster adoption and measurable results.
AI adoption is growing fast across industries. Companies that understand AI Agents and LLMs get a head start. They can automate tasks. They can scale content. They gain insights more effectively than competitors.
This gives them an advantage in speed, efficiency, and decision-making.
Deploying the right AI tool saves time, money, and improves your business outcomes.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI Agent is a system that can act on its own to achieve specific goals. It works independently. It connects with multiple systems. It makes decisions that improve efficiency. It reduces the need for constant human supervision.
Think of it like a smart assistant. It knows what to do. It checks all your tools. It takes action without you telling it every step.
It can manage workflows. It monitors performance. It learns from feedback to get better over time.
AI Agents often integrate LLMs, machine learning, and APIs. This means they can handle complex tasks. They respond to changes in real time. They continuously improve performance.
They become a self-sustaining system that grows with your business.
Characteristics of AI Agents
Goal-Oriented: AI Agents focus on achieving specific outcomes. They automate customer support. They manage inventory. They optimize ad campaigns. This saves time and improves accuracy.
Autonomous: They make decisions without constant human oversight. They interpret real-time data. They adjust actions. They maintain consistent performance, even in dynamic environments.
Environment-Aware: AI Agents monitor surroundings continuously. They react to user interactions. They respond to system data or external events. This keeps workflows optimized. It reduces errors or downtime.
Learning Over Time: AI Agents improve as they operate. They analyze performance feedback. They adjust strategies. They learn from new data to increase long-term business value.
Think of it this way: AI Agents act like self-driving cars for your business. They guide tasks automatically while learning to perform better over time.
How AI Agents Work
AI Agents perceive their environment. They reason about possible actions. They execute steps to reach goals.
They combine real-time data, rules, and AI models to make decisions. This reduces human intervention while staying efficient and accurate.
They integrate with business tools. They pull data from CRMs, analytics dashboards, or operational systems. This creates connected workflows. It automates repetitive tasks. It provides insights that free human teams to focus on creative or strategic work.
Over time, AI Agents analyze results. They learn what works best. They adjust strategies. This allows businesses to scale without adding staff or increasing costs.
Pros and Cons of AI Agents
| Feature | Pros | Cons |
| Efficiency | Automates repetitive tasks and frees up team time | Initial setup may require significant investment in software, infrastructure, and training |
| Consistency | Executes processes accurately every time | Integration with multiple systems can be complex |
| Scalability | Handles growing workloads without proportional human resources | Depends heavily on clean, high-quality data |
| Decision-making | Uses data to optimize actions and improve ROI | Limited creativity, can’t replicate human intuition |
AI Agents are powerful for structured, repeatable tasks. But they need quality data and proper setup to shine.
What Is an LLM?

A Large Language Model (LLM) is a type of AI that understands and generates human-like text. It analyzes huge amounts of text data. It identifies patterns. It produces content that makes sense in context.
Unlike AI Agents, LLMs don’t act on their own. They need prompts or instructions from humans or other systems.
They are excellent for generating content. They answer questions. They summarize documents. They automate responses at scale.
Think of an LLM as a super-smart writer or assistant. It can draft emails, reports, or chatbot replies based on instructions you give it. It does the writing, but you or another system still guides its actions.
Characteristics of LLMs
Language Expertise: Understands grammar, context, and nuance. Produces high-quality content for blogs, emails, social media, and more.
Pattern Recognition: Spots linguistic patterns across large datasets. Predicts text. Summarizes information. Answers questions accurately.
Scalable Output: Can generate large volumes of consistent, coherent content quickly. This is great for businesses with extensive communications needs.
Prompt-Dependent: Requires clear instructions or prompts to perform tasks. Human or AI guidance ensures outputs align with business objectives.
Think of it this way: LLMs are your writing experts. They work best when given clear instructions and goals.
How LLMs Work
LLMs learn by analyzing billions of text examples. They detect relationships between words, phrases, and ideas. They predict the next word or generate coherent responses.
During training, LLMs use supervised and unsupervised learning. They optimize patterns. They understand context. They improve accuracy over time.
This creates outputs that feel natural, relevant, and aligned with expectations.
Businesses use LLMs for content generation, summarization, and natural language understanding. They create marketing emails. They generate FAQ responses. They condense long reports into short, actionable insights.
Key Differences Between AI Agents and LLMs
Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right tool. It helps integrate systems effectively. It helps achieve maximum efficiency, automation, and content quality.
Scope: AI Agents handle multiple tasks autonomously. LLMs focus on language tasks only.
Autonomy: AI Agents act independently. LLMs need prompts.
Learning: AI Agents learn from feedback and improve actions. LLMs learn from text patterns and refine outputs.
Application: AI Agents automate workflows. LLMs generate content and provide text-based insights.
Think of AI Agents as doers and LLMs as communicators. Together, they cover both action and language.
AI Agents vs LLMs: Quick Comparison
| Feature | AI Agent | LLM |
| Scope | Autonomous across multiple tasks and systems | Specializes in text generation and understanding |
| Autonomy | High – acts independently based on data and goals | Low – depends on prompts or integration |
| Learning | Adaptive from feedback and environment | Pattern-based from large datasets |
| Applications | Workflow automation, decision-making, monitoring | Content creation, summarization, language analysis |
| Integration | Connects tools, APIs, and data sources | Embedded in broader AI systems |
| Value | Saves time, reduces errors, scales efficiency | Produces high-quality language outputs at scale |
The two technologies complement each other. AI Agents handle execution while LLMs provide communication intelligence.
Real-Life Applications of AI Agents
AI Agents are used in industries needing fast decision-making and complex workflows. They automate repetitive tasks. They monitor operations. They execute multi-step processes. This reduces costs and boosts efficiency.
Customer Service
AI Agents handle queries. They escalate issues. They learn from past interactions. This improves accuracy, response time, and customer satisfaction. It lowers staffing needs.
Marketing
Marketing teams use AI Agents to monitor campaigns. They adjust ad spend. They deliver personalized recommendations. Analyzing data in real-time helps maximize ROI. It frees staff for creative work.
Operations and Supply Chain
Operations teams benefit as AI Agents track inventory. They predict shortages. They coordinate deliveries. This ensures continuity. It minimizes errors. It maintains productivity in fast-moving environments.
AI Agents excel in automating complex, repetitive, or multi-step business processes.
Real-Life Applications of LLMs
LLMs generate content, summarize data, and understand language at scale. They create marketing copy, product descriptions, documentation, and chatbot responses. They do this consistently and quickly.
Customer Support
Customer support teams rely on LLMs to answer FAQs. They summarize tickets. They respond across channels. Maintaining a natural tone ensures a uniform, high-quality user experience.
Knowledge Management
For knowledge management, LLMs summarize reports. They analyze large datasets. Decision-makers get insights quickly without reading long documents.
Content Marketing
In content marketing, LLMs produce blog posts, social media updates, and email campaigns. They follow brand guidelines. They create engaging outputs. Teams focus on strategy and creativity.
LLMs shine in text-heavy tasks where quality, consistency, and speed are essential.
Collaborative Use Cases of AI Agents and LLMs
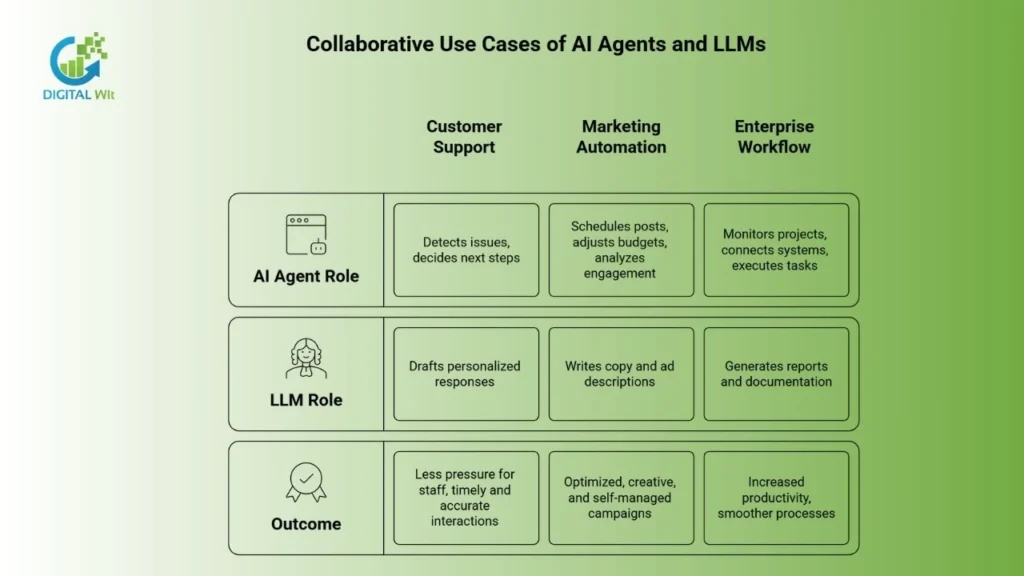
Combining AI Agents with LLMs creates a seamless system. AI Agents handle workflow steps. LLMs supply context-aware text. Together, they execute tasks efficiently and communicate naturally.
Customer Support Example
AI Agents detect issues and decide next steps. LLMs draft personalized responses. Staff experience less pressure. Users get timely, accurate interactions.
Marketing Automation
AI Agents schedule posts. They adjust budgets. They analyze engagement. LLMs write copy and ad descriptions. Campaigns become optimized, creative, and largely self-managed.
Enterprise Workflow
AI Agents monitor projects. They connect systems. They execute operational tasks. LLMs generate reports and documentation. Productivity rises. Processes become smoother across departments.
AI Agents and LLMs together combine action and communication for maximum business efficiency.
The Role of LLMs in AI Agents
LLMs act as the “language brain” of AI Agents. They generate coherent text for communication, summaries, and documents. This allows AI Agents to act and communicate without relying fully on humans.
For example, an AI Agent in HR can draft onboarding emails. It creates feedback summaries. It updates policies using LLMs.
The agent executes tasks while the LLM ensures language quality, tone, and clarity. This creates a fully automated workflow.
Integrating LLMs also helps AI Agents interpret instructions. They produce step-by-step plans. They generate insights. Combining both tools creates end-to-end automation. This improves efficiency and reduces errors.
LLMs provide the language intelligence AI Agents need to perform complex tasks that involve both action and communication.
Maximizing ROI: Why Understanding AI vs LLM Pays Off
Better Decisions: Select technology tailored to the problem. This reduces wasted effort.
Smarter Automation: AI predicts. LLM communicates. Combining them multiplies efficiency.
Content at Scale: LLMs turn raw data into persuasive messaging and engaging content.
Future-Proofing: Businesses understanding these differences gain a competitive edge in innovation and market positioning.
Final Thoughts
AI Agents handle actions. LLMs handle language. Together they transform how businesses operate.
By understanding their differences and leveraging them strategically, you can:
- Streamline workflows
- Scale content effortlessly
- Achieve higher ROI
This makes your operations smarter, faster, and more competitive.
At Digital Wit, we guide businesses through the complex AI landscape:
- Implement AI workflows that improve operational efficiency
- Deploy LLMs for content, chatbots, and knowledge automation
- Combine tools strategically for maximum ROI without guesswork
Ready to scale your marketing, automation, and content strategy? Start your AI journey with Digital Wit today.