Discover the Power of SaaS Semantic SEO to rank higher using SaaS SEO strategies from Digital Wit
In the rapidly changing digital marketing landscape, focusing solely on keyword optimization is no longer sufficient. SaaS Semantic SEO is essential for SaaS companies aiming to stand out in a competitive market.
Semantic SEO goes beyond traditional keyword targeting by focusing on the intent behind user queries, context, and related concepts.
SaaS companies implementing semantic SEO strategies have reported up to a 30-50% increase in organic traffic within 6 to 12 months. This is due to better alignment with search intent and improved relevance for long-tail keywords.
This approach not only helps your content rank higher in search results but also enhances user experience by providing more relevant and comprehensive information.
In this guide, we’ll explore how SaaS companies can leverage Semantic SEO to boost their online visibility, improve engagement, and drive more qualified leads.
Introduction to SaaS Semantic SEO
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a cloud-based service where software applications are delivered over the internet. Instead of purchasing and installing software on individual computers, users access the software via a web browser.
SaaS providers host and maintain the software, infrastructure, and data, offering features such as regular updates, scalability, and accessibility from any location with an internet connection. Users typically pay a subscription fee to use the software on a monthly or annual basis. Common examples of SaaS include platforms like Google Workspace, Salesforce, and Microsoft 365.
Companies using semantic SEO often see a 20-40% increase in featured snippet appearances and other SERP features, leading to higher click-through rates (CTR) and visibility for their content.

Semantic SEO is Your Business Key
AI is transforming search. With Semantic SEO, align your content to AI’s understanding, ensuring better rankings and visibility. Stay ahead and drive results.
What is Saas SEO?
SaaS SEO (Software as a Service Search Engine Optimization) refers to the specific strategies and techniques used to optimize a SaaS company’s website and content to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
The goal is to attract more organic (non-paid) traffic, which can then be converted into leads, trials, and customers. We have to follow not only SEO best practices but also make SEO strategies for saas industry.
Content optimized semantically often results in a 15-25% increase in average time on page. This is because semantically rich content is more likely to match user intent, keeping visitors engaged.
Semantic seo important in SaaS
- Long-Term Growth: Unlike paid advertising, SEO can provide a sustainable source of traffic over time.
- Cost-Effective: While it requires an investment in time and resources, the cost per lead for SEO can be lower than that of paid channels.
- Builds Authority: High rankings for competitive keywords establish the company as a leader in its field.
- Increases Visibility: SEO helps SaaS companies reach a broader audience that may not be aware of their product.
SaaS SEO is a crucial part of a digital marketing strategy for any software company looking to grow its online presence and customer base.
SaaS businesses using semantic SEO have seen 25-35% improvements in rankings for long-tail and related keywords, as search engines better understand the context of their content.
By matching content more closely to user intent through semantic SEO, some SaaS companies have reported a 10-20% increase in conversion rates from organic search traffic.
Relevance of Semantic SEO for SaaS companies
Semantic SEO allows for 25-30% more efficient content creation, as content clusters and pillar pages reduce redundancy and make it easier to cover related topics comprehensively.
Semantic SEO is increasingly becoming a cornerstone of effective digital marketing strategies, especially for SaaS companies. This advanced form of search engine optimization goes beyond traditional keyword targeting to understand the context, intent, and relationships between words and concepts. Here’s why Semantic SEO is particularly relevant for SaaS companies:
1. Enhanced Understanding of User Intent
SaaS customers often search with specific needs in mind. By focusing on Semantic SEO, SaaS companies can better align their content with the intent behind search queries. This means that your content will be more likely to answer the precise questions your potential customers are asking, leading to higher engagement and satisfaction.
2. Improved Content Relevance and Authority
Search engines now prioritize content that demonstrates experience, expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). Semantic SEO helps SaaS companies create content that is contextually rich and relevant, addressing not just isolated keywords but entire topics comprehensively. This can improve your content’s authority in the eyes of search engines, leading to better rankings.
3. Greater Focus on Long-Tail Keywords and Phrases
Semantic SEO naturally favors long-tail keywords and conversational phrases. For SaaS companies, this means capturing more targeted traffic, as users often search for specific solutions to niche problems. Optimizing for these long-tail queries can drive highly qualified leads who are closer to making a purchasing decision.
4. Better User Experience (UX)
A key goal of Semantic SEO is to enhance the overall user experience. By delivering content that answers users’ questions more effectively and efficiently, SaaS companies can improve the usability of their websites. This can lead to longer dwell times, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates.
5. Alignment with Voice Search and AI-Powered Search
Voice search is becoming more prevalent, especially with the rise of digital assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. Semantic SEO helps SaaS companies optimize for the natural, conversational queries users make through voice search. This also aligns well with AI-powered search algorithms that prioritize context and intent.
6. Competitive Edge in a Saturated Market
The SaaS market is highly competitive, with many companies offering similar solutions.Semantic SEO allows you to differentiate your content by focusing on unique angles, comprehensive solutions, and user-centric approaches. This can set your SaaS offering apart from competitors who may still rely on outdated keyword-focused strategies.
7. Support for Complex Buyer Journeys
SaaS buyers often go through a multi-step decision-making process. Semantic SEO enables you to create content that addresses each stage of the buyer’s journey, from awareness to consideration to decision. By understanding and responding to the nuances of user intent, you can guide potential customers more effectively through this process.
8. Future-Proofing Your SEO Strategy
Search algorithms are continually evolving, with a clear trend toward understanding context and user intent. By adopting Semantic SEO, SaaS companies can future-proof their SEO strategies, ensuring that their content remains relevant and effective even as search engines become more sophisticated.
For SaaS companies, embracing Semantic SEO is not just an option but a necessity in today’s digital landscape. It allows you to create more meaningful connections with your audience, improve your search rankings, and ultimately drive more qualified traffic and conversions. By focusing on the deeper meanings and relationships between concepts, Semantic SEO ensures that your SaaS product is visible, valuable, and aligned with the needs of your target audience.
Understanding Semantic SEO : Digital Wit
In the competitive SaaS industry, having a well-defined SEO approach is crucial for standing out in the crowded market. A leading SaaS marketing agency Digital Wit understands the importance of leveraging a topical map and semantic content strategy to create a robust semantic content network.
This advanced approach to SEO not only aligns with the latest trends in the SEO industry but also ensures that your marketing efforts are optimized within your SaaS marketing budget. By integrating these strategies, SEO providers can help SaaS companies achieve higher visibility and sustainable growth in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Implementing semantic SEO strategies has led to 10-15% lower bounce rates for many SaaS companies, as users find the content more relevant to their needs.
By establishing topical authority through semantic SEO, some SaaS companies have seen a 15-20% increase in backlinks from authoritative domains, enhancing overall site authority.
Principles of Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO focuses on understanding and optimizing for the intent and context behind search queries rather than just targeting specific keywords. This approach aligns more closely with how search engines, particularly Google, interpret and rank content. Here are the key principles of Semantic SEO:
1. Understanding User Intent
– Principle: Search engines aim to deliver content that best matches the user’s intent. Semantic SEO prioritizes understanding the different types of user intent, such as informational (seeking knowledge), navigational (finding a specific site), transactional (purchasing something), or commercial investigation (researching products or services before buying).
– Application: When creating content, focus on what the user is really searching for, not just the keywords they are using. This involves answering questions, solving problems, and addressing the specific needs of your audience.
2. Topic Clustering and Content Hubs
– Principle: Instead of creating isolated pieces of content targeting individual keywords, Semantic SEO encourages the creation of interconnected content that revolves around a central topic. This strategy is known as topic clustering.
– Application: Develop pillar content (a comprehensive guide on a broad topic) and cluster content (related articles or pages that dive deeper into subtopics). All these pieces should be interlinked, providing a rich, interconnected user experience and signaling to search engines that your site covers the topic comprehensively.
3. Entity Optimization
– Principle: Search engines increasingly rely on entities (people, places, things, or concepts) rather than just keywords to understand content. An entity is any concept that is singular, unique, and well-defined.
– Application: Incorporate entities into your content to provide clear and structured information. This can be done by mentioning known entities and linking to authoritative sources or using structured data (schema markup) to help search engines better understand the context of your content.
4. Contextual Relevance
– Principle: Semantic SEO is about the context surrounding keywords, not just the keywords themselves. Search engines look at the surrounding words, phrases, and topics to understand the full meaning of the content.
– Application: Ensure that your content is contextually rich by using related terms, synonyms, and phrases that naturally expand on the main topic. Avoid keyword stuffing, and instead, aim for a natural flow of language that reflects how people actually search and think.
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
– Principle: Search engines use NLP to better understand human language, including syntax, semantics, and sentiment. This allows them to interpret content more like a human reader.
– Application: Write content that is clear, concise, and easy to read. Use a conversational tone when appropriate and focus on readability. Tools like Google’s BERT algorithm are designed to understand the nuances of language, so content that mimics natural speech patterns can perform better.
6. Structured Data and Schema Markup
– Principle: Structured data and schema markup help search engines understand the content of your pages more accurately by providing additional context.
– Application: Implement schema markup on your website to highlight key pieces of information such as product details, reviews, FAQs, and events. This not only helps search engines interpret your content better but also enhances your chances of appearing in rich snippets, which can boost click-through rates.
7. Comprehensive Content Creation
– Principle: Semantic SEO favors in-depth, comprehensive content that covers a topic thoroughly. Search engines reward content that answers a user’s query in full, reducing the need for them to look elsewhere.
– Application: Create long-form content that addresses all aspects of a topic. Include related subtopics, FAQs, and supplementary information to make your content the definitive resource on the subject.
8. User Experience and Engagement
– Principle: Search engines increasingly consider user engagement signals (such as time on page, bounce rate, and click-through rate) as indicators of content quality and relevance.
– Application: Focus on creating content that is not only informative but also engaging. Use multimedia elements like images, videos, and infographics to enhance the user experience. Ensure your site is easy to navigate and mobile-friendly to reduce bounce rates and keep users engaged.
9. Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI)
– Principle: LSI keywords are terms and phrases that are semantically related to your main keyword. These help search engines understand the topic of your content better.
– Application: Incorporate LSI keywords naturally throughout your content to provide additional context. These can include synonyms, related words, and commonly associated phrases that enhance the depth and breadth of your content.
10. Continuous Optimization and Adaptation
– Principle: The digital landscape and search algorithms are constantly evolving. Semantic SEO requires ongoing optimization and adaptation to stay effective.
– Application: Regularly update your content to keep it fresh and relevant. Analyze performance data to identify areas for improvement and adapt your SEO strategies in response to changes in search algorithms and user behavior.
Semantic SEO is a forward-thinking approach that prioritizes the meaning and context behind content, aligning closely with how modern search engines operate. By focusing on these principles, businesses can create content that is not only optimized for search engines but also provides a richer, more valuable experience for users.
Differences between traditional SEO and Semantic SEO
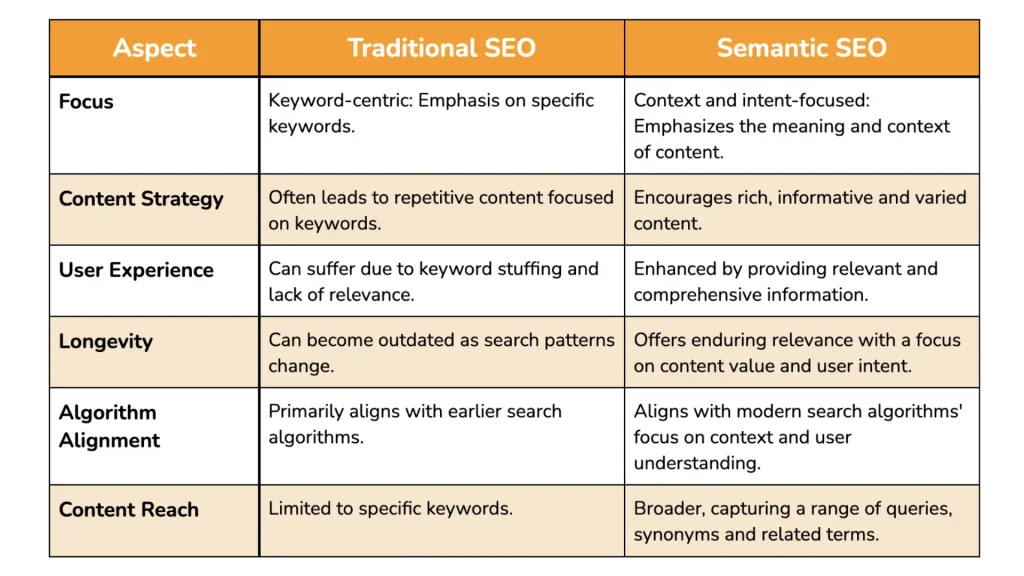
Traditional SEO and Semantic SEO both aim to improve a website’s visibility in search engine results, but they differ significantly in their approaches, strategies, and the outcomes they seek to achieve. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
1. Focus on Keywords vs. Focus on User Intent
– Traditional SEO:
– Primarily focuses on targeting specific keywords that users might search for. The goal is to optimize content around these exact keywords to rank higher in search results.
– Example: If the target keyword is “best project management software,” traditional SEO would focus on repeating this exact phrase throughout the content.
– Semantic SEO:
– Emphasizes understanding and optimizing for the intent behind the search queries. It goes beyond keywords to consider the context and meaning of the user’s search, aiming to provide comprehensive answers.
– Example: For the same keyword “best project management software,” Semantic SEO would focus on covering related topics such as features, comparisons, use cases, and user reviews to satisfy the user’s intent.
2. Keyword Stuffing vs. Contextual Relevance
– Traditional SEO:
– Often involves keyword stuffing, where the target keyword is used repeatedly in the content to signal relevance to search engines. This approach can lead to unnatural, awkward content that doesn’t prioritize user experience.
– Example: Overusing the phrase “best project management software” unnaturally within the text, even if it disrupts the flow of content.
– Semantic SEO:
– Prioritizes contextual relevance and natural language use. Instead of repeating the exact keyword, related terms, synonyms, and phrases are used to create a rich and contextually relevant piece of content.
– Example: Using terms like “top project management tools,” “software for managing projects,” or “best tools for project management” in a way that naturally fits into the content.
3. Page-Level Optimization vs. Topic Clustering
– Traditional SEO:
– Focuses on optimizing individual pages for specific keywords. Each page is treated as a separate entity targeting a particular search term.
– Example: Creating multiple separate pages for each keyword variation, like “best project management software,” “top project management tools,” and “best software for project management.”
– Semantic SEO:
– Emphasizes topic clustering, where a main topic (pillar content) is covered in-depth and supported by related subtopics (cluster content). This approach creates a network of interconnected content that provides comprehensive coverage of a subject.
– Example: Creating a pillar page on “Project Management Software” and linking to related cluster pages on topics like “Features of Project Management Tools,” “How to Choose the Right Project Management Software,” and “Case Studies on Project Management Software.”
4. Exact Match Keywords vs. Entities and Concepts
– Traditional SEO:
– Relies heavily on exact match keywords and their variations. The focus is on optimizing for these specific terms rather than the broader concept they represent.
– Example: Optimizing for exact keywords like “buy laptop online” and “cheap laptops for sale.”
– Semantic SEO:
– Focuses on entities (people, places, things) and broader concepts. Search engines recognize entities and their relationships, so content is optimized around these rather than just keywords.
– Example: Instead of focusing only on “buy laptop online,” Semantic SEO would optimize for the broader concept of “buying electronics online,” including related entities like brands, models, and types of laptops.
5. Isolated Optimization vs. Holistic Optimization
– Traditional SEO:
– Tends to focus on optimizing individual elements like meta tags, headings, and content separately. The approach is more about ticking off checklists for on-page factors.
– Example: Ensuring that the keyword appears in the title tag, meta description, H1 tag, and throughout the content.
– Semantic SEO:
– Takes a holistic approach to optimization, considering how all elements of a page work together to convey meaning and relevance. It focuses on overall user experience and the depth of content.
– Example: Crafting content that naturally includes the target topic in the title, headings, and throughout the text while also considering related topics, user engagement, and readability.
6. Single Keywords vs. Long-Tail and Conversational Phrases
– Traditional SEO:
– Primarily targets single, high-volume keywords. The strategy is to rank for these specific terms, which can be highly competitive.
– Example: Targeting “CRM software” as the primary keyword.
– Semantic SEO:
– Prioritizes long-tail keywords and conversational phrases that reflect how users naturally search. This approach captures more specific queries and provides better alignment with user intent.
– Example: Targeting phrases like “what is the best CRM software for small businesses” or “how to choose CRM software for startups.”
7. Algorithm Manipulation vs. User-Centric Content
– Traditional SEO:
– Historically involved trying to manipulate search engine algorithms through tactics like keyword density, backlink building, and exact match anchor text. The focus was more on pleasing the algorithm than the user.
– Example: Building numerous low-quality backlinks with exact match anchor text to manipulate rankings.
– Semantic SEO:
– Centers on creating user-centric content that naturally aligns with how search engines are designed to function. The focus is on delivering value to the user, which in turn is recognized and rewarded by search engines.
– Example: Creating content that genuinely helps users solve a problem or answer a question, leading to natural backlinks and higher engagement metrics.
8. Local Optimization vs. Global Contextual Relevance
– Traditional SEO:
– Often focuses on local optimization techniques, such as including local keywords and optimizing for Google My Business.
– Example: Using location-based keywords like “best pizza in Dhaka.”
– Semantic SEO:
– Focuses on broader contextual relevance that applies globally or across different contexts. It’s about understanding how your content fits into the larger conversation within your industry.
– Example: Discussing “the global pizza market” or “how pizza trends differ around the world,” with a specific mention of New York as a key location.
While “Traditional SEO” is more about optimizing for specific keywords and following a formulaic approach, “Semantic SEO” is about understanding and catering to the deeper meaning behind search queries.
It focuses on context, intent, and the relationships between topics, leading to a more holistic, user-centered approach to content creation and optimization. By embracing Semantic SEO, businesses can better align with how search engines and users are evolving, resulting in more sustainable and effective SEO strategies.
Benefits of Semantic SEO for SaaS businesses
Semantic SEO offers several significant advantages for SaaS businesses, helping them improve their online presence, attract more qualified leads, and ultimately grow their customer base. Here are the key benefits:
1. Better Alignment with User Intent
– Benefit: Semantic SEO focuses on understanding and addressing the intent behind users’ search queries, not just the keywords they use.
– Impact: SaaS businesses can create content that directly answers the specific questions and pain points of potential customers. This alignment leads to higher engagement, as users are more likely to find the information they need, reducing bounce rates and increasing time on site.
2. Improved Search Engine Rankings
– Benefit: By optimizing content for topics and entities rather than just keywords, Semantic SEO helps SaaS businesses rank for a broader range of relevant search queries.
– Impact: This approach enhances visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs) and increases the chances of ranking for long-tail keywords and related searches. As a result, SaaS businesses can capture more organic traffic and outperform competitors who rely on traditional SEO techniques.
3. Enhanced Content Relevance and Authority
– Benefit: Semantic SEO encourages the creation of comprehensive, in-depth content that covers topics thoroughly.
– Impact: This boosts the relevance and authority of SaaS websites in the eyes of search engines, leading to higher rankings for competitive keywords. Additionally, authoritative content attracts backlinks from other websites, further enhancing search engine performance.
4. Increased Organic Traffic
– Benefit: With a focus on long-tail keywords, user intent, and topic clustering, Semantic SEO drives more targeted and qualified traffic to a SaaS website.
– Impact: SaaS businesses benefit from attracting users who are actively seeking specific solutions or information related to their products, increasing the likelihood of conversions and reducing the cost per acquisition compared to paid channels.
5. Higher Conversion Rates
– Benefit: By delivering content that closely matches the needs and expectations of users, Semantic SEO helps build trust and credibility.
– Impact: This trust translates into higher conversion rates as potential customers are more likely to engage with the content, sign up for trials, request demos, or purchase subscriptions. Semantic SEO helps SaaS businesses move users through the sales funnel more effectively.
6. Better User Experience (UX)
– Benefit: Semantic SEO emphasizes creating content that is easy to read, understand, and navigate, contributing to a positive user experience.
– Impact: A better UX leads to longer sessions, lower bounce rates, and more satisfied users. For SaaS businesses, this can mean stronger customer retention, higher lifetime value, and more positive word-of-mouth referrals.
7. Competitive Advantage
– Benefit: SaaS is a highly competitive market, and businesses that adopt Semantic SEO can gain an edge over competitors who still rely on outdated SEO practices.
– Impact: By focusing on comprehensive, user-centered content and optimizing for modern search algorithms, SaaS companies can differentiate themselves, attract more organic traffic, and build stronger relationships with their audience.
8. Future-Proofing SEO Strategy
– Benefit: Search engines are increasingly prioritizing semantic understanding and user intent. Semantic SEO is aligned with these trends and is more resilient to algorithm changes.
– Impact: SaaS businesses that adopt Semantic SEO are better positioned to maintain and improve their rankings over time, regardless of changes to search engine algorithms. This reduces the risk of sudden drops in traffic and ensures long-term success.
9. Greater Content Discoverability
– Benefit: Semantic SEO enhances content discoverability by optimizing for related terms, synonyms, and entities.
– Impact: SaaS content is more likely to appear in a wider range of search queries, increasing the chances of being discovered by users who may not have been familiar with the brand or product. This broad reach helps SaaS businesses tap into new audiences and expand their market share.
10. Increased Rich Snippet Opportunities
– Benefit: By utilizing structured data and focusing on comprehensive content, Semantic SEO increases the likelihood of earning rich snippets in search results.
– Impact: Rich snippets, such as featured snippets, FAQs, and knowledge panels, enhance visibility and click-through rates (CTR) by providing users with immediate answers directly in the SERPs. For SaaS businesses, this can mean more exposure and higher traffic without needing to rank first organically.
Semantic SEO offers a multitude of benefits for SaaS businesses, from better search engine rankings and increased organic traffic to higher conversion rates and improved user experience. By focusing on user intent, content relevance, and holistic optimization, SaaS companies can effectively differentiate themselves in a crowded market, attract more qualified leads, and drive sustainable growth.
Core Components of Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO is centered on understanding and optimizing for user intent, going beyond traditional keyword targeting to create more contextually relevant content. It involves key components like topic clusters, which organize content around central themes and interlink related subtopics to provide comprehensive coverage.
Entity optimization and structured data are also crucial, as they help search engines better understand the content by defining key concepts and relationships. Additionally, Natural Language Processing (NLP) ensures that content is both readable and aligned with conversational search queries. Overall, Semantic SEO enhances content relevance, depth, and user experience, leading to improved search engine rankings and engagement.
- Keyword Research and Optimization
Keyword research for Semantic SEO focuses on understanding user intent and identifying related concepts rather than just individual keywords. Optimization involves integrating these keywords naturally within context-rich content, using topic clusters, and emphasizing synonyms and related terms to enhance relevance and improve search engine understanding.
- Importance of relevant keywords
Relevant keywords are crucial for connecting content with user search queries, ensuring that your website appears in search results for topics your audience cares about. By targeting the right keywords, you attract more qualified traffic, improve user engagement, and increase the likelihood of conversions and higher search rankings.
- Using long-tail keywords and LSI terms
Using long-tail keywords and Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) terms allows you to capture more specific, intent-driven search queries. Long-tail keywords target niche audiences with higher conversion potential, while LSI terms enhance content relevance by incorporating related concepts, helping search engines better understand and rank your content in context.
- Content Creation and Optimization
Content creation and optimization for Semantic SEO involve producing in-depth, contextually rich content that addresses user intent. This includes organizing content into topic clusters, using natural language, and incorporating relevant keywords, synonyms, and entities. The goal is to enhance content relevance, improve user experience, and achieve better search engine rankings.
- Creating high-quality, user-focused content
Creating high-quality, user-focused content involves understanding your audience’s needs and providing valuable, informative, and engaging material that addresses their pain points. This approach builds trust and credibility, encourages longer site visits, and fosters higher engagement, ultimately leading to better search engine rankings and increased conversions.
- Structuring content with semantic markup
Structuring content with semantic markup for Semantic SEO involves using HTML tags like `<header>`, `<article>`, and `<section>` to define the purpose of each content element. This helps search engines better understand the context and relationships within your content, improving indexing, enhancing visibility in SERPs, and increasing the likelihood of rich snippet appearances.
- On-Page SEO
On-page SEO for Semantic SEO involves optimizing content to align with user intent, ensuring that it’s contextually relevant and comprehensive. This includes using topic clusters, incorporating long-tail keywords and LSI terms, and structuring content with semantic markup. Additionally, it emphasizes a clear content hierarchy, internal linking, and enhancing readability to improve both user experience and search engine understanding.
- Meta tags, headers, and schema markup
Meta tags, headers, and schema markup are essential for improving content visibility and search engine understanding. Meta tags provide brief descriptions for search results, headers structure content for better readability and relevance, and schema markup adds contextual data, enabling rich snippets and enhancing the way search engines interpret and display your content.
- Internal linking strategies
Internal linking strategies involve connecting related content within your website to enhance navigation, distribute link equity, and guide users through relevant topics. Effective internal linking improves SEO by helping search engines understand site structure and content relationships, boosting overall site authority.
Are you ready?
Our tried and tested approach to Search Engine Optimization
Implementing Semantic SEO in SaaS
Implementing Semantic SEO in SaaS involves optimizing content for user intent, using topic clusters, and leveraging structured data to enhance search engine understanding, improving rankings, visibility, and lead generation. We have to develop semantic seo important strategies for properly marketing the saas products and services .
- Steps to integrate Semantic SEO in SaaS
Some important points are as follows :
– Identify user intent to align content with search queries.
– Create topic clusters around central themes.
– Optimize content with relevant keywords, entities, and natural language.
– Implement structured data for better search engine understanding.
– Establish a strong internal linking structure for improved navigation and authority.
- Tools for Semantic SEO
– Google Search Console: Monitors site performance, indexing, and search query data.
– SEMrush: Provides keyword research, content analysis, and topic clustering.
– Ahrefs: Tracks backlinks, keyword rankings, and competitor analysis.
– SurferSEO: Analyzes on-page SEO and recommends content optimization based on SERP data.
– Yoast SEO Offers on-page optimization and schema markup for WordPress sites.
– MarketMuse: Assists in content planning, gap analysis, and topic modeling.
– Google NLP API: Analyzes content for entities, sentiment, and syntax.
– Screaming Frog: Crawls websites to audit technical SEO, including internal linking.
Case studies of successful SaaS companies using Semantic SEO
In the SaaS industry , SEO is the process how companies rank in the search engines. Semantic search engine optimization can be used in the process. Some case studies are as follows :
Case Study 1: HubSpot – Leveraging Semantic SEO for Inbound Marketing
Background:
HubSpot, a leading SaaS provider of inbound marketing and sales software, faced the challenge of ranking for highly competitive keywords in the digital marketing space. With a growing number of competitors, simply targeting exact-match keywords was no longer sufficient.
Approach:
HubSpot implemented a Semantic SEO strategy focused on creating comprehensive content clusters around broad topics. Instead of targeting individual keywords, HubSpot created pillar pages that covered a broad topic in depth, such as “Inbound Marketing,” and then linked to cluster content that delved into subtopics like “Content Marketing,” “Email Marketing,” and “SEO.”
Results:
This semantic approach allowed HubSpot to rank for a wide variety of long-tail keywords and related search queries. Their content began to appear in featured snippets, rich results, and other high-visibility SERP features. Over time, HubSpot saw a significant increase in organic traffic, with many pages ranking in the top positions for highly competitive terms.
The strategy also positioned HubSpot as an authoritative source in the marketing space, driving more qualified leads to their SaaS platform.
Case Study 2: Ahrefs – Dominating the SEO Tool Market through Semantic SEO
Background:
Ahrefs, a popular SEO tool provider, needed to distinguish itself in a crowded market. With numerous competitors also vying for visibility, Ahrefs needed a strategy that would help them capture more organic traffic and demonstrate their expertise.
Approach:
Ahrefs employed a Semantic SEO strategy by creating detailed guides, tutorials, and blog posts centered around broad topics like “SEO,” “Backlinking,” and “Keyword Research.
” Their content was structured to address user intent by answering common questions, providing actionable insights, and linking to related resources. They utilized internal linking to create a web of interconnected content, which signaled to search engines the depth and relevance of their content on these topics.
Results:
The use of Semantic SEO allowed Ahrefs to rank highly for numerous related queries and long-tail keywords, driving a substantial increase in organic traffic. Their content became a go-to resource for SEO professionals, enhancing their brand authority.
As a result, Ahrefs not only saw growth in website traffic but also in customer acquisition, as more users turned to their platform for SEO solutions.
Case Study 3: Shopify – Enhancing E-Commerce SEO with Semantic Content
Background:
Shopify, a leading e-commerce SaaS platform, sought to increase visibility and attract more small businesses looking to build online stores. With the rise of e-commerce, Shopify needed to ensure that their content could capture a diverse range of search queries from potential customers.
Approach:
Shopify adopted a Semantic SEO approach by creating a wide range of content that addressed the different stages of the e-commerce journey. They developed content clusters around broad topics such as “E-commerce,” “Dropshipping,” and “Online Store Setup,
” with each cluster addressing various subtopics and frequently asked questions. Shopify also optimized content for intent-based searches, ensuring that their articles, guides, and how-to content met the needs of users at different stages of the buying process.
Results:
Through Semantic SEO, Shopify was able to capture a broad spectrum of search traffic, from beginners looking to start an online store to advanced users seeking to optimize their e-commerce sites.
This strategy not only increased their organic traffic but also improved their search engine rankings for a diverse set of keywords. Shopify’s content became a trusted resource in the e-commerce space, leading to a higher conversion rate and a significant boost in new customer sign-ups.
Keyword Research for SaaS Semantic SEO
Keyword research for SaaS Semantic SEO involves identifying keywords that align with user intent and the specific needs of your target audience. Focus on long-tail keywords, industry-specific terms, and related concepts. This approach ensures content relevance, enhances visibility in niche markets, and improves the likelihood of capturing qualified leads.
- Identifying high-intent keywords
Identifying high-intent keywords involves finding search terms that indicate strong purchasing or decision-making intent, directly aligning with user needs.
- Utilizing customer pain points and solutions
Understanding customer pain points is crucial for tailoring solutions that meet their needs. By identifying and addressing these issues through targeted strategies, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Utilizing feedback and data ensures solutions are effective, turning challenges into opportunities for growth and strengthening the overall customer experience.
- Competitor analysis and keyword gaps
Competitor analysis reveals keyword gaps by identifying terms competitors target but your site misses. Addressing these gaps allows you to optimize content, improve SEO, and gain a competitive edge in search rankings.
Content Strategy for SaaS Semantic SEO
A content strategy for SaaS Semantic SEO involves creating content that aligns with user intent and relevant semantic keywords. By focusing on context and meaning, rather than just specific keywords, you improve search visibility and user engagement. This approach enhances relevance and authority, driving targeted traffic and conversions for SaaS products.
- Creating topic clusters and pillar content
Creating topic clusters and pillar content involves organizing content around central themes and linking related articles. This strategy improves SEO, enhances user experience, and establishes authority by providing comprehensive, interconnected information.
- Addressing user intent in content
Addressing user intent in content means creating material that directly answers users’ queries and needs. By aligning content with what users are searching for, you improve relevance, engagement, and satisfaction.
- Optimizing for featured snippets and People Also Ask boxes
Optimizing for featured snippets and People Also Ask boxes requires crafting clear, concise answers to common questions. Use structured data, bullet points, and headings to enhance visibility and capture user interest effectively.
Technical SEO for SaaS Platforms
Technical SEO for SaaS platforms involves optimizing site structure, improving load speeds, and ensuring mobile-friendliness. Implementing proper indexing, fixing broken links, and enhancing security with HTTPS are crucial for better search engine visibility and user experience in SaaS applications.
- Site architecture and navigation
Site architecture and navigation focus on creating a clear, logical structure and intuitive menus, enhancing user experience and search engine indexing.
- Page load speed and mobile optimization
Page load speed and mobile optimization are crucial for user experience and SEO, ensuring fast, responsive, and accessible content on all devices.
- Structured data and rich snippets
Structured data uses schema markup to provide search engines with detailed content information, enabling the display of rich snippets. These enhanced search results improve visibility, click-through rates, and user engagement.
Measuring the Success of Semantic SEO
Creating an effective SaaS SEO strategy is essential for driving growth in the competitive SaaS industry. The founder of holistic SEO emphasizes the importance of integrating different SEO approaches, including on-page and off-page SEO, to address the unique SEO needs of each business. Keywords in SEO, combined with the importance of semantic SEO and content, are crucial in optimizing your strategy.
SaaS marketing experts from Digital Wit agree that a balanced SaaS marketing mix should include SEO and UX considerations to enhance user experience. By focusing on KPIs for SaaS and leveraging SEO to improve visibility, your SEO work will contribute to overall SEO performance. Ultimately, ensuring that your SEO strategy stays aligned with the evolving landscape will be helpful in maintaining a competitive edge in the SEO and SaaS space.
Measuring the success of Semantic SEO involves tracking metrics like organic traffic growth, keyword rankings, user engagement, conversion rates, and the number of rich snippets, indicating improved search visibility and relevance.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) for SEO
Key performance indicators (KPIs) for SEO include organic traffic, keyword rankings, bounce rate, conversion rate, average session duration, click-through rate (CTR), and backlink quality, all reflecting the effectiveness of SEO efforts.
- Tracking and analyzing traffic and conversions
Tracking and analyzing traffic and conversions involve using tools like Google Analytics to monitor user behavior, source of traffic, and conversion paths, helping to assess SEO performance and optimize strategies for better results.
- Adjusting strategies based on performance data
Adjusting strategies based on performance data involves reviewing SEO metrics, identifying trends, and making data-driven changes to content, keywords, and site structure. This helps to optimize outcomes, ensuring continuous improvement in search performance.
Future Trends in Semantic SEO for SaaS
Future trends in Semantic SEO for SaaS include increased focus on AI-driven content optimization, voice search adaptation, enhanced entity recognition, and deeper integration of user intent analysis, leading to more personalized and relevant search experiences.
- AI and machine learning in SEO
AI and machine learning in SEO enhance search algorithms by better understanding user intent, automating keyword research, optimizing content, and predicting trends, leading to more accurate and personalized search results.
- Voice search optimization
Voice search optimization involves tailoring content to be easily understood by voice-activated devices. Focus on natural language, conversational phrases, and question-based queries. Optimize for local SEO and ensure fast loading times. Structured data and clear, concise answers improve visibility, making it easier for voice assistants to deliver relevant results.
- Evolving search algorithms and their impact
Evolving search algorithms enhance search result accuracy and relevance. They influence SEO strategies, necessitating continuous adaptation to new ranking criteria and user behavior shifts, impacting content visibility and engagement.
Summary of key points
SaaS Semantic SEO involves optimizing software-as-a-service (SaaS) content to align with user intent and search engine understanding. Semantic SEO helps search engines to find the best results. Some Key points include:
1. Semantic Keywords: Focus on user intent and contextual relevance rather than just keywords.
2. Content Quality: Create comprehensive, valuable content addressing user needs.
3. Structured Data: Use schema markup to help search engines understand and index content.
4. User Experience: Improve site navigation and readability for better engagement.
5. Voice Search Optimization: Tailor content for conversational queries and natural language.
6. Regular Updates: Continuously update content to reflect the latest trends and user needs.
Importance of continuous learning and adaptation in SEO
In the ever-evolving world of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), continuous learning and adaptation are paramount for success. SEO is not a static field; it’s constantly shaped by changes in search engine algorithms, evolving user behaviors, and emerging technologies.
This dynamism means that strategies and techniques that worked well yesterday might not be effective today, and what works today might become obsolete tomorrow.
Continuous learning allows SEO professionals to stay abreast of the latest trends, tools, and best practices. Search engines like Google frequently update their algorithms to improve the quality and relevance of search results.
Staying informed about these updates helps SEO practitioners adjust their strategies accordingly, ensuring their content remains visible and competitive. For example, understanding updates like Google’s BERT or MUM can significantly impact how content is optimized for natural language processing and user intent.
Adaptation is equally crucial. The SEO landscape includes shifts in user behavior, such as the increasing importance of voice search or the rise of mobile-first indexing. Adapting to these changes means refining strategies to meet new demands and preferences.
Additionally, as new technologies emerge—such as AI-driven tools or advancements in data analytics—SEO professionals need to integrate these innovations to maintain a competitive edge.
Moreover, continuous learning fosters creativity and problem-solving. It enables SEO experts to experiment with novel approaches and analyze results to determine what works best in various contexts. This iterative process leads to more effective strategies and improved outcomes.
In summary, the importance of continuous learning and adaptation in SEO cannot be overstated. Staying updated with industry changes and being flexible in response to new developments ensures that SEO strategies remain relevant and effective, ultimately driving better results for businesses and their digital presence.